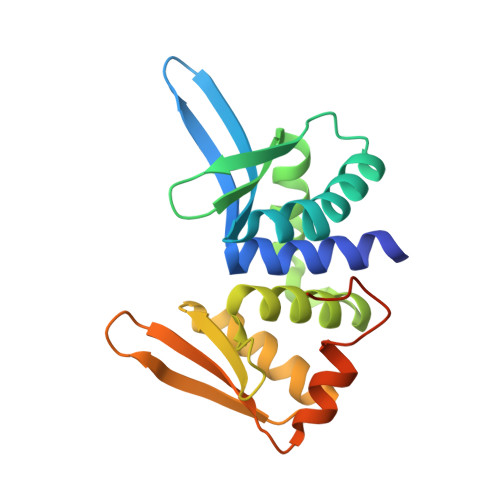
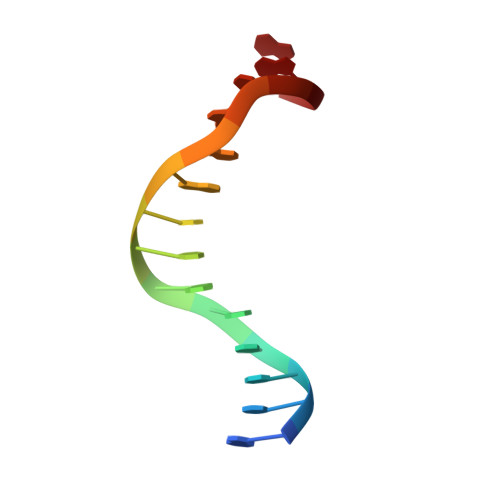
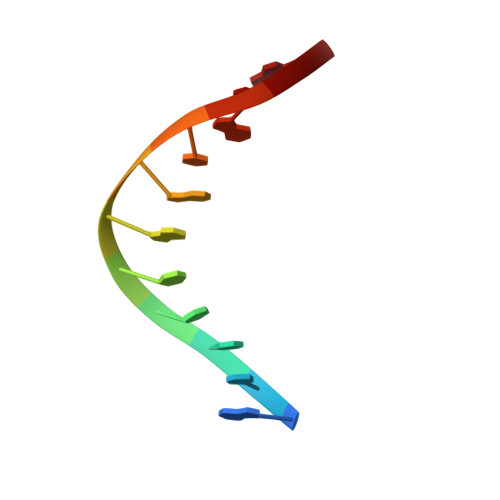
Engineering a Nickase on the Homing Endonuclease I-Dmoi Scaffold.
Molina, R., Marcaida, M.J., Redondo, P., Marenchino, M., Duchateau, P., D'Abramo, M., Montoya, G., Prieto, J.(2015) J Biol Chem 290: 18534
- PubMed: 26045557
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.658666
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
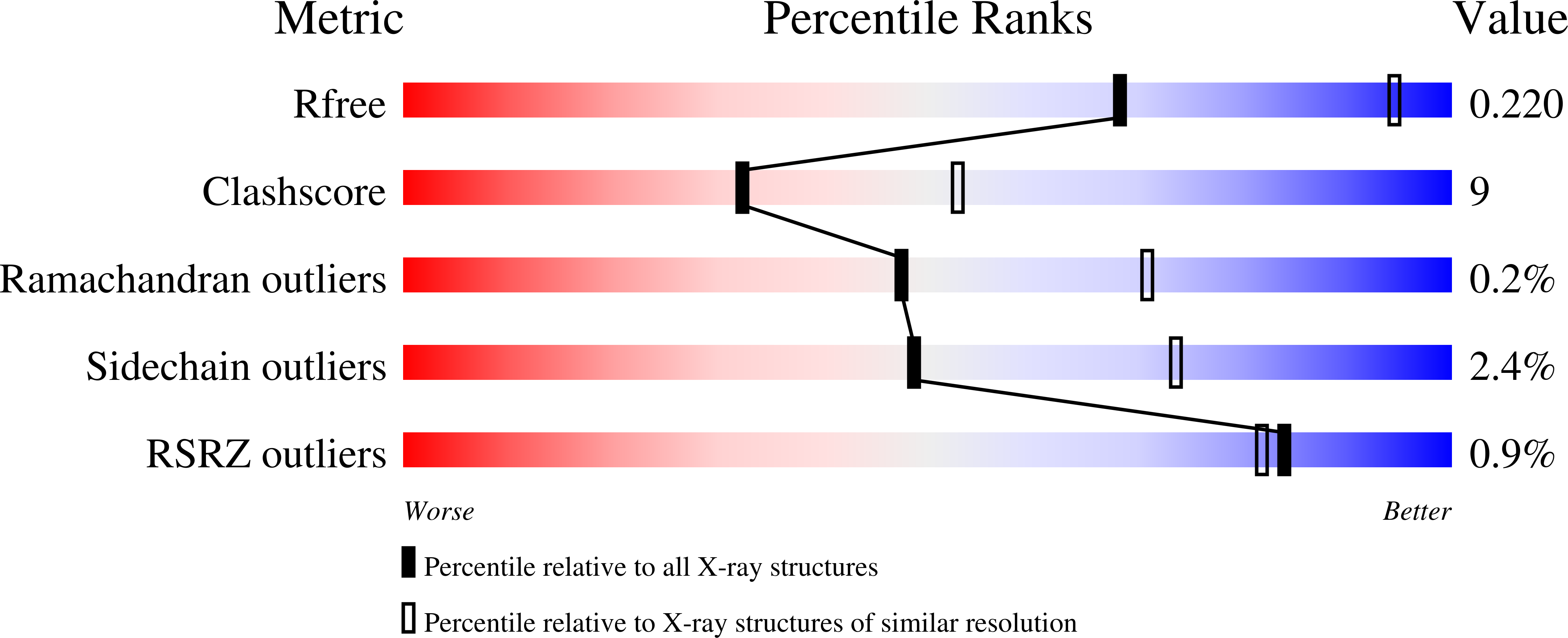
5AK9, 5AKF, 5AKM, 5AKN - PubMed Abstract:
Homing endonucleases are useful tools for genome modification because of their capability to recognize and cleave specifically large DNA targets. These endonucleases generate a DNA double strand break that can be repaired by the DNA damage response machinery. The break can be repaired by homologous recombination, an error-free mechanism, or by non-homologous end joining, a process susceptible to introducing errors in the repaired sequence. The type of DNA cleavage might alter the balance between these two alternatives. The use of "nickases" producing a specific single strand break instead of a double strand break could be an approach to reduce the toxicity associated with non-homologous end joining by promoting the use of homologous recombination to repair the cleavage of a single DNA break. Taking advantage of the sequential DNA cleavage mechanism of I-DmoI LAGLIDADG homing endonuclease, we have developed a new variant that is able to cut preferentially the coding DNA strand, generating a nicked DNA target. Our structural and biochemical analysis shows that by decoupling the action of the catalytic residues acting on each strand we can inhibit one of them while keeping the other functional.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Macromolecular Crystallography Group and.