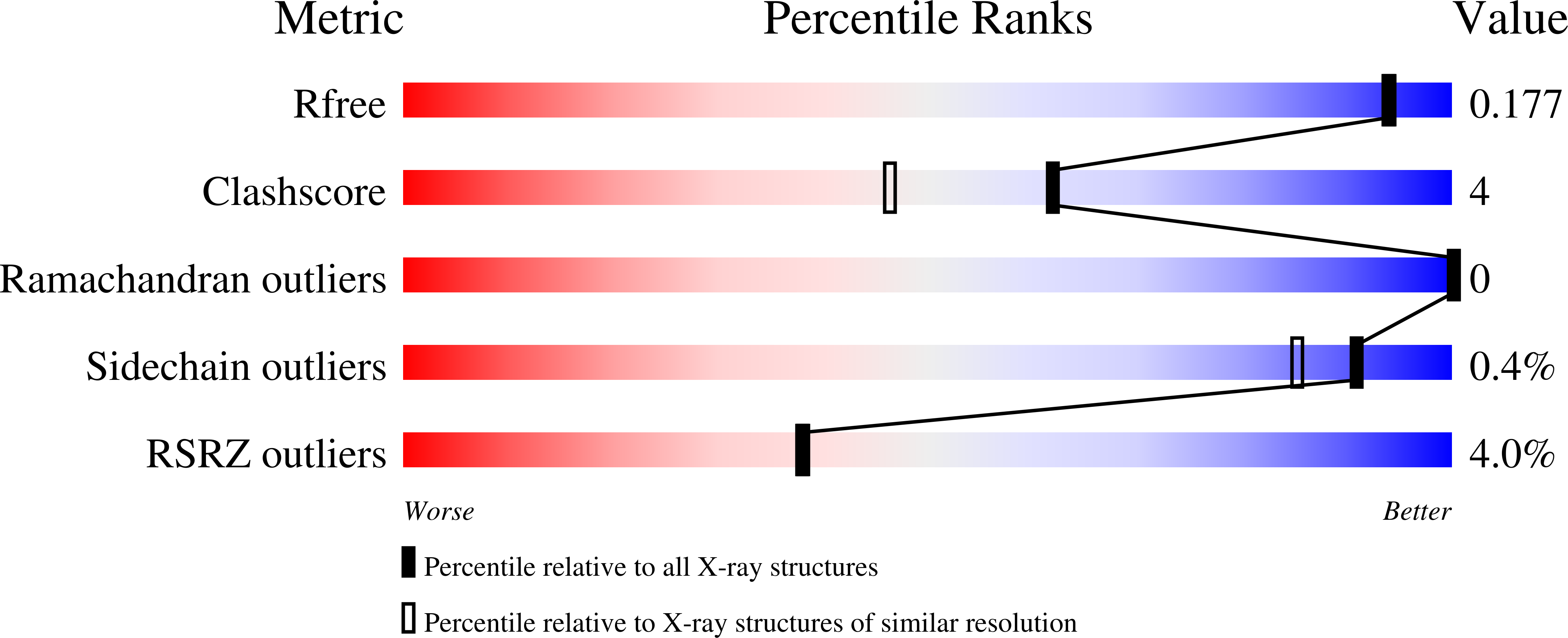
Bacterial Renalase: Structure and Kinetics of an Enzyme with 2- and 6-Dihydro-beta-NAD(P) Oxidase Activity from Pseudomonas phaseolicola.
Hoag, M.R., Roman, J., Beaupre, B.A., Silvaggi, N.R., Moran, G.R.(2015) Biochemistry 54: 3791-3802
- PubMed: 26016690
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00451
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4ZCC, 4ZCD - PubMed Abstract:
Despite a lack of convincing in vitro evidence and a number of sound refutations, it is widely accepted that renalase is an enzyme unique to animals that catalyzes the oxidative degradation of catecholamines in blood in order to lower vascular tone. Very recently, we identified isomers of β-NAD(P)H as substrates for renalase (Beaupre, B. A. et al. (2015) Biochemistry, 54, 795-806). These molecules carry the hydride equivalent on the 2 or 6 position of the nicotinamide base and presumably arise in nonspecific redox reactions of nicotinamide dinucleotides. Renalase serves to rapidly oxidize these isomers to form β-NAD(P)⁺ and then pass the electrons to dioxygen, forming H₂O₂. We have also shown that these substrate molecules are highly inhibitory to dehydrogenase enzymes and thus have proposed an intracellular metabolic role for this enzyme. Here, we identify a renalase from an organism without a circulatory system. This bacterial form of renalase has the same substrate specificity profile as that of human renalase but, in terms of binding constant (K(d)), shows a marked preference for substrates derived from β-NAD⁺. 2-dihydroNAD(P) substrates reduce the enzyme with rate constants (k(red)) that greatly exceed those for 6-dihydroNAD(P) substrates. Taken together, k(red)/K(d) values indicate a minimum 20-fold preference for 2DHNAD. We also offer the first structures of a renalase in complex with catalytically relevant ligands β-NAD⁺ and β-NADH (the latter being an analogue of the substrate(s)). These structures show potential electrostatic repulsion interactions with the product and a unique binding orientation for the substrate nicotinamide base that is consistent with the identified activity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee, 3210 North Cramer Street, Milwaukee, Wisconsin 53211-3209, United States.