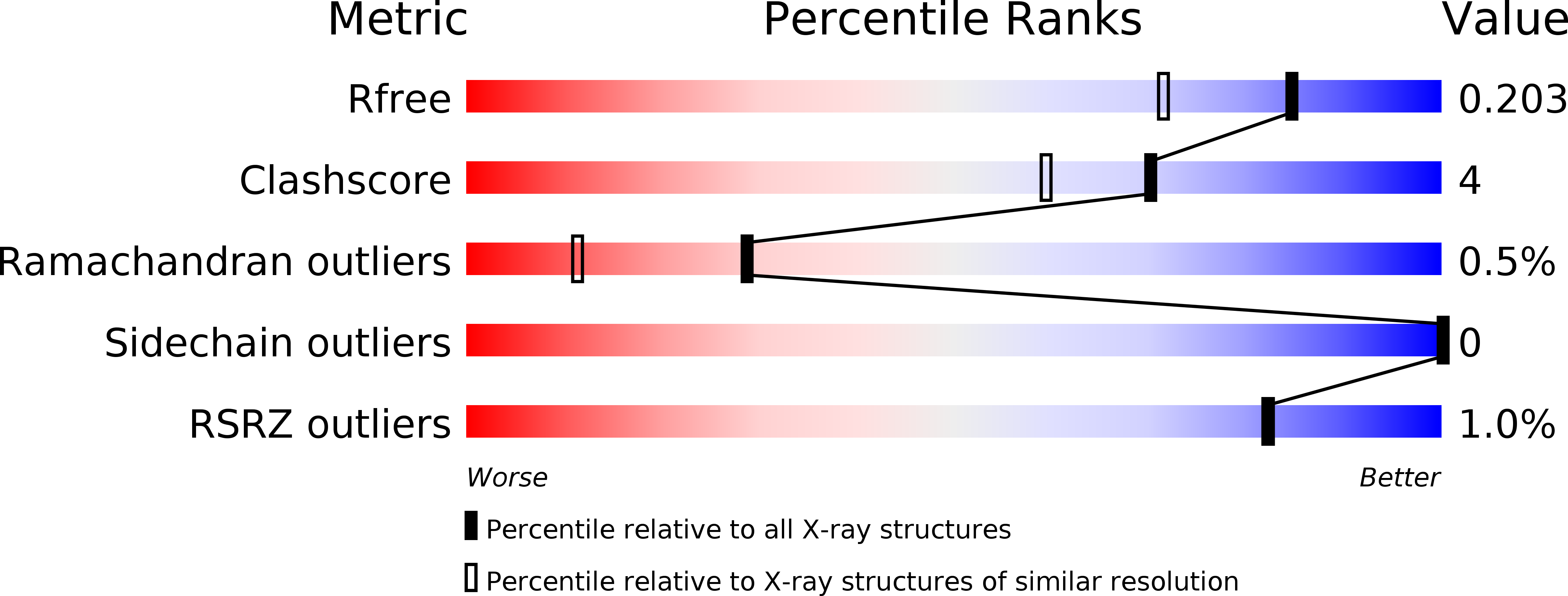
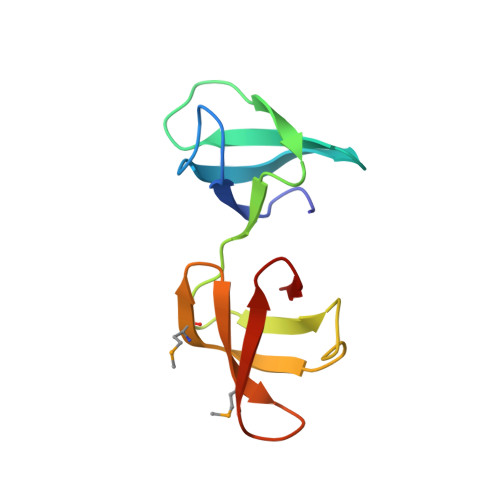
Structures and Functions of the Multiple KOW Domains of Transcription Elongation Factor Spt5.
Meyer, P.A., Li, S., Zhang, M., Yamada, K., Takagi, Y., Hartzog, G.A., Fu, J.(2015) Mol Cell Biol 35: 3354-3369
- PubMed: 26217010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00520-15
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4YTK, 4YTL - PubMed Abstract:
The eukaryotic Spt4-Spt5 heterodimer forms a higher-order complex with RNA polymerase II (and I) to regulate transcription elongation. Extensive genetic and functional data have revealed diverse roles of Spt4-Spt5 in coupling elongation with chromatin modification and RNA-processing pathways. A mechanistic understanding of the diverse functions of Spt4-Spt5 is hampered by challenges in resolving the distribution of functions among its structural domains, including the five KOW domains in Spt5, and a lack of their high-resolution structures. We present high-resolution crystallographic results demonstrating that distinct structures are formed by the first through third KOW domains (KOW1-Linker1 [K1L1] and KOW2-KOW3) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Spt5. The structure reveals that K1L1 displays a positively charged patch (PCP) on its surface, which binds nucleic acids in vitro, as shown in biochemical assays, and is important for in vivo function, as shown in growth assays. Furthermore, assays in yeast have shown that the PCP has a function that partially overlaps that of Spt4. Synthesis of our results with previous evidence suggests a model in which Spt4 and the K1L1 domain of Spt5 form functionally overlapping interactions with nucleic acids upstream of the transcription bubble, and this mechanism may confer robustness on processes associated with transcription elongation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, Wisconsin, USA.