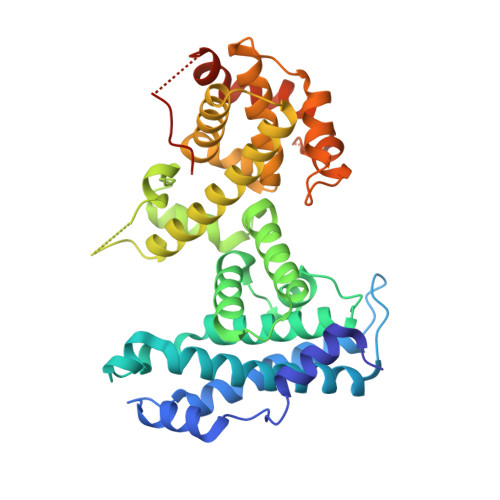
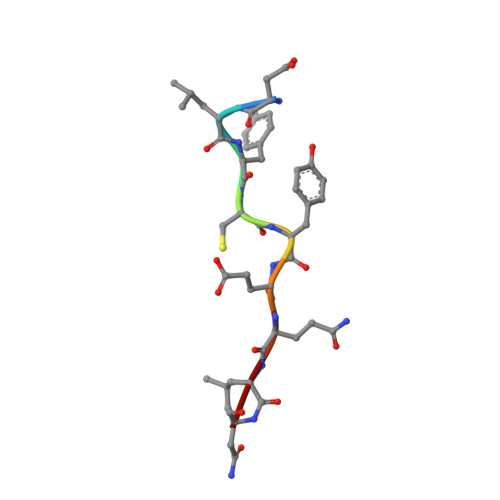
Structural mechanisms of DREAM complex assembly and regulation.
Guiley, K.Z., Liban, T.J., Felthousen, J.G., Ramanan, P., Litovchick, L., Rubin, S.M.(2015) Genes Dev 29: 961-974
- PubMed: 25917549
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.257568.114
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4YOO, 4YOS, 4YOZ - PubMed Abstract:
The DREAM complex represses cell cycle genes during quiescence through scaffolding MuvB proteins with E2F4/5 and the Rb tumor suppressor paralog p107 or p130. Upon cell cycle entry, MuvB dissociates from p107/p130 and recruits B-Myb and FoxM1 for up-regulating mitotic gene expression. To understand the biochemical mechanisms underpinning DREAM function and regulation, we investigated the structural basis for DREAM assembly. We identified a sequence in the MuvB component LIN52 that binds directly to the pocket domains of p107 and p130 when phosphorylated on the DYRK1A kinase site S28. A crystal structure of the LIN52-p107 complex reveals that LIN52 uses a suboptimal LxSxExL sequence together with the phosphate at nearby S28 to bind the LxCxE cleft of the pocket domain with high affinity. The structure explains the specificity for p107/p130 over Rb in the DREAM complex and how the complex is disrupted by viral oncoproteins. Based on insights from the structure, we addressed how DREAM is disassembled upon cell cycle entry. We found that p130 and B-Myb can both bind the core MuvB complex simultaneously but that cyclin-dependent kinase phosphorylation of p130 weakens its association. Together, our data inform a novel target interface for studying MuvB and p130 function and the design of inhibitors that prevent tumor escape in quiescence.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of California at Santa Cruz, Santa Cruz, California 95064, USA;