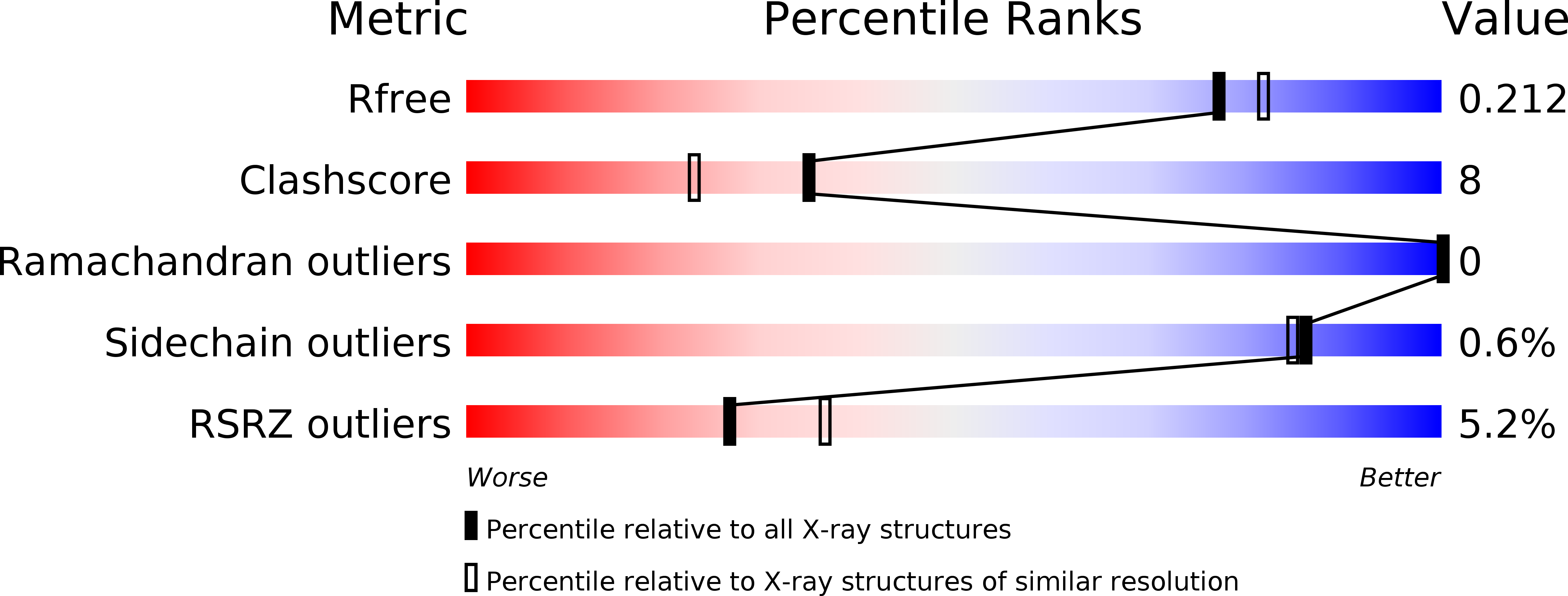
Structural and functional analysis of two di-domain aromatase/cyclases from type II polyketide synthases.
Caldara-Festin, G., Jackson, D.R., Barajas, J.F., Valentic, T.R., Patel, A.B., Aguilar, S., Nguyen, M., Vo, M., Khanna, A., Sasaki, E., Liu, H.W., Tsai, S.C.(2015) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112: E6844-E6851
- PubMed: 26631750
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1512976112
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4XRT, 4XRW - PubMed Abstract:
Aromatic polyketides make up a large class of natural products with diverse bioactivity. During biosynthesis, linear poly-β-ketone intermediates are regiospecifically cyclized, yielding molecules with defined cyclization patterns that are crucial for polyketide bioactivity. The aromatase/cyclases (ARO/CYCs) are responsible for regiospecific cyclization of bacterial polyketides. The two most common cyclization patterns are C7-C12 and C9-C14 cyclizations. We have previously characterized three monodomain ARO/CYCs: ZhuI, TcmN, and WhiE. The last remaining uncharacterized class of ARO/CYCs is the di-domain ARO/CYCs, which catalyze C7-C12 cyclization and/or aromatization. Di-domain ARO/CYCs can further be separated into two subclasses: "nonreducing" ARO/CYCs, which act on nonreduced poly-β-ketones, and "reducing" ARO/CYCs, which act on cyclized C9 reduced poly-β-ketones. For years, the functional role of each domain in cyclization and aromatization for di-domain ARO/CYCs has remained a mystery. Here we present what is to our knowledge the first structural and functional analysis, along with an in-depth comparison, of the nonreducing (StfQ) and reducing (BexL) di-domain ARO/CYCs. This work completes the structural and functional characterization of mono- and di-domain ARO/CYCs in bacterial type II polyketide synthases and lays the groundwork for engineered biosynthesis of new bioactive polyketides.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Biology and Biochemistry, University of California, Irvine, CA 92697; Department of Chemistry, University of California, Irvine, CA 92697; Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of California, Irvine, CA 92697;