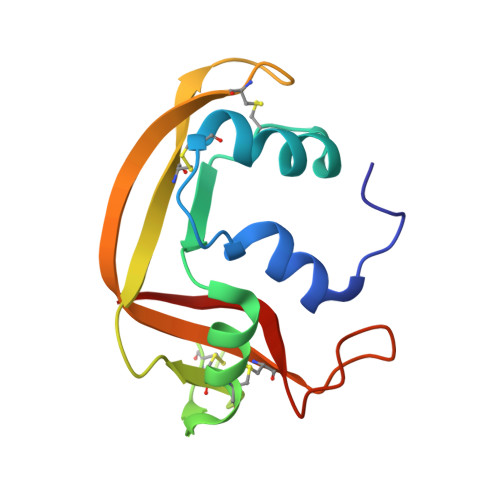
The first crystal structure of human RNase 6 reveals a novel substrate-binding and cleavage site arrangement.
Prats-Ejarque, G., Arranz-Trullen, J., Blanco, J.A., Pulido, D., Nogues, M.V., Moussaoui, M., Boix, E.(2016) Biochem J 473: 1523-1536
- PubMed: 27013146
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20160245
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4X09 - PubMed Abstract:
Human RNase 6 is a cationic secreted protein that belongs to the RNase A superfamily. Its expression is induced in neutrophils and monocytes upon bacterial infection, suggesting a role in host defence. We present here the crystal structure of RNase 6 obtained at 1.72 Å (1 Å=0.1 nm) resolution, which is the first report for the protein 3D structure and thereby setting the basis for functional studies. The structure shows an overall kidney-shaped globular fold shared with the other known family members. Three sulfate anions bound to RNase 6 were found, interacting with residues at the main active site (His(15), His(122) and Gln(14)) and cationic surface-exposed residues (His(36), His(39), Arg(66) and His(67)). Kinetic characterization, together with prediction of protein-nucleotide complexes by molecular dynamics, was applied to analyse the RNase 6 substrate nitrogenous base and phosphate selectivity. Our results reveal that, although RNase 6 is a moderate catalyst in comparison with the pancreatic RNase type, its structure includes lineage-specific features that facilitate its activity towards polymeric nucleotide substrates. In particular, enzyme interactions at the substrate 5' end can provide an endonuclease-type cleavage pattern. Interestingly, the RNase 6 crystal structure revealed a novel secondary active site conformed by the His(36)-His(39) dyad that facilitates the polynucleotide substrate catalysis.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Faculty of Biosciences, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, E-08193 Cerdanyola del Vallès, Spain.