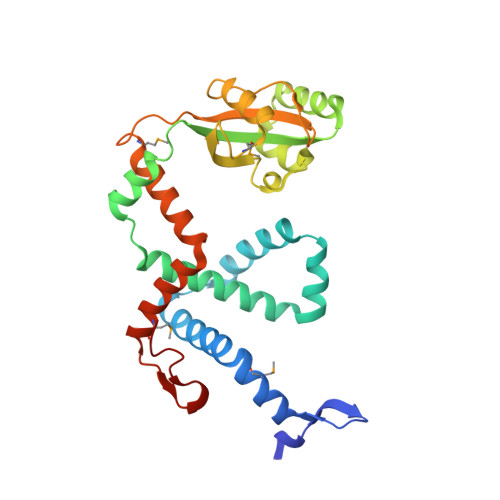
Dimeric Structure of the Bacterial Extracellular Foldase PrsA.
Jakob, R.P., Koch, J.R., Burmann, B.M., Schmidpeter, P.A., Hunkeler, M., Hiller, S., Schmid, F.X., Maier, T.(2015) J Biol Chem 290: 3278-3292
- PubMed: 25525259
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.622910
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4WO7 - PubMed Abstract:
Secretion of proteins into the membrane-cell wall space is essential for cell wall biosynthesis and pathogenicity in Gram-positive bacteria. Folding and maturation of many secreted proteins depend on a single extracellular foldase, the PrsA protein. PrsA is a 30-kDa protein, lipid anchored to the outer leaflet of the cell membrane. The crystal structure of Bacillus subtilis PrsA reveals a central catalytic parvulin-type prolyl isomerase domain, which is inserted into a larger composite NC domain formed by the N- and C-terminal regions. This domain architecture resembles, despite a lack of sequence conservation, both trigger factor, a ribosome-binding bacterial chaperone, and SurA, a periplasmic chaperone in Gram-negative bacteria. Two main structural differences are observed in that the N-terminal arm of PrsA is substantially shortened relative to the trigger factor and SurA and in that PrsA is found to dimerize in a unique fashion via its NC domain. Dimerization leads to a large, bowl-shaped crevice, which might be involved in vivo in protecting substrate proteins from aggregation. NMR experiments reveal a direct, dynamic interaction of both the parvulin and the NC domain with secretion propeptides, which have been implicated in substrate targeting to PrsA.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Biozentrum, Universität Basel, Klingelbergstrasse 50/70, 4056 Basel, Switzerland and roman.jakob@unibas.ch.