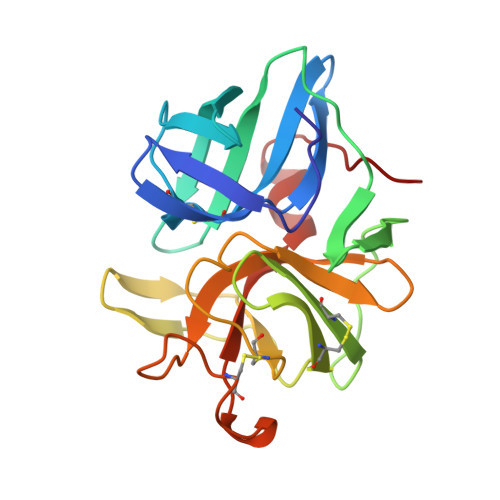
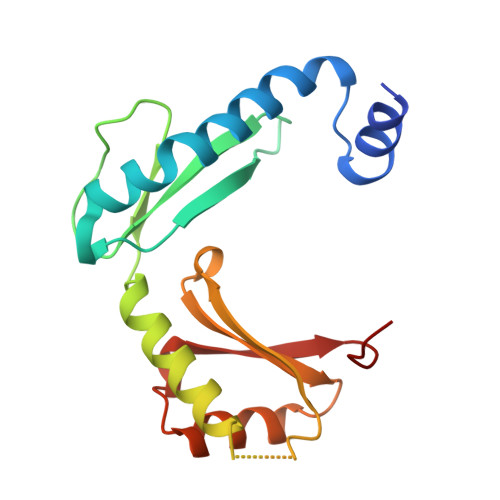
Structure of alpha-lytic protease complexed with its pro region.
Sauter, N.K., Mau, T., Rader, S.D., Agard, D.A.(1998) Nat Struct Biol 5: 945-950
- PubMed: 9808037
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/2919
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2PRO, 3PRO, 4PRO - PubMed Abstract:
While the majority of proteins fold rapidly and spontaneously to their native states, the extracellular bacterial protease alpha-lytic protease (alphaLP) has a t(1/2) for folding of approximately 2,000 years, corresponding to a folding barrier of 30 kcal mol(-1). AlphaLP is synthesized as a pro-enzyme where its pro region (Pro) acts as a foldase to stabilize the transition state for the folding reaction. Pro also functions as a potent folding catalyst when supplied as a separate polypeptide chain, accelerating the rate of alphaLP folding by a factor of 3 x 10(9). In the absence of Pro, alphaLP folds only partially to a stable molten globule-like intermediate state. Addition of Pro to this intermediate leads to rapid formation of native alphaLP. Here we report the crystal structures of Pro and of the non-covalent inhibitory complex between Pro and native alphaLP. The C-shaped Pro surrounds the C-terminal beta-barrel domain of the folded protease, forming a large complementary interface. Regions of extensive hydration in the interface explain how Pro binds tightly to the native state, yet even more tightly to the folding transition state. Based on structural and functional data we propose that a specific structural element in alphaLP is largely responsible for the folding barrier and suggest how Pro can overcome this barrier.
Organizational Affiliation:
Howard Hughes Medical Institute, University of California, San Francisco, 94143-0448, USA.