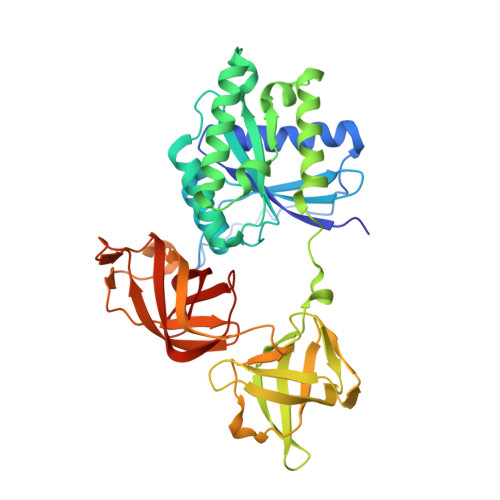
Structure of the Acinetobacter baumannii Dithiol Oxidase DsbA Bound to Elongation Factor EF-Tu Reveals a Novel Protein Interaction Site.
Premkumar, L., Kurth, F., Duprez, W., Grftehauge, M.K., King, G.J., Halili, M.A., Heras, B., Martin, J.L.(2014) J Biol Chem 289: 19869-19880
- PubMed: 24860094
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.571737
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4P3Y - PubMed Abstract:
The multidrug resistant bacterium Acinetobacter baumannii is a significant cause of nosocomial infection. Biofilm formation, that requires both disulfide bond forming and chaperone-usher pathways, is a major virulence trait in this bacterium. Our biochemical characterizations show that the periplasmic A. baumannii DsbA (AbDsbA) enzyme has an oxidizing redox potential and dithiol oxidase activity. We found an unexpected non-covalent interaction between AbDsbA and the highly conserved prokaryotic elongation factor, EF-Tu. EF-Tu is a cytoplasmic protein but has been localized extracellularly in many bacterial pathogens. The crystal structure of this complex revealed that the EF-Tu switch I region binds to the non-catalytic surface of AbDsbA. Although the physiological and pathological significance of a DsbA/EF-Tu association is unknown, peptides derived from the EF-Tu switch I region bound to AbDsbA with submicromolar affinity. We also identified a seven-residue DsbB-derived peptide that bound to AbDsbA with low micromolar affinity. Further characterization confirmed that the EF-Tu- and DsbB-derived peptides bind at two distinct sites. These data point to the possibility that the non-catalytic surface of DsbA is a potential substrate or regulatory protein interaction site. The two peptides identified in this work together with the newly characterized interaction site provide a novel starting point for inhibitor design targeting AbDsbA.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Institute for Molecular Bioscience, Division of Chemistry and Structural Biology, University of Queensland, St. Lucia, Queensland 4067, Australia p.lakshmanane@uq.edu.au.