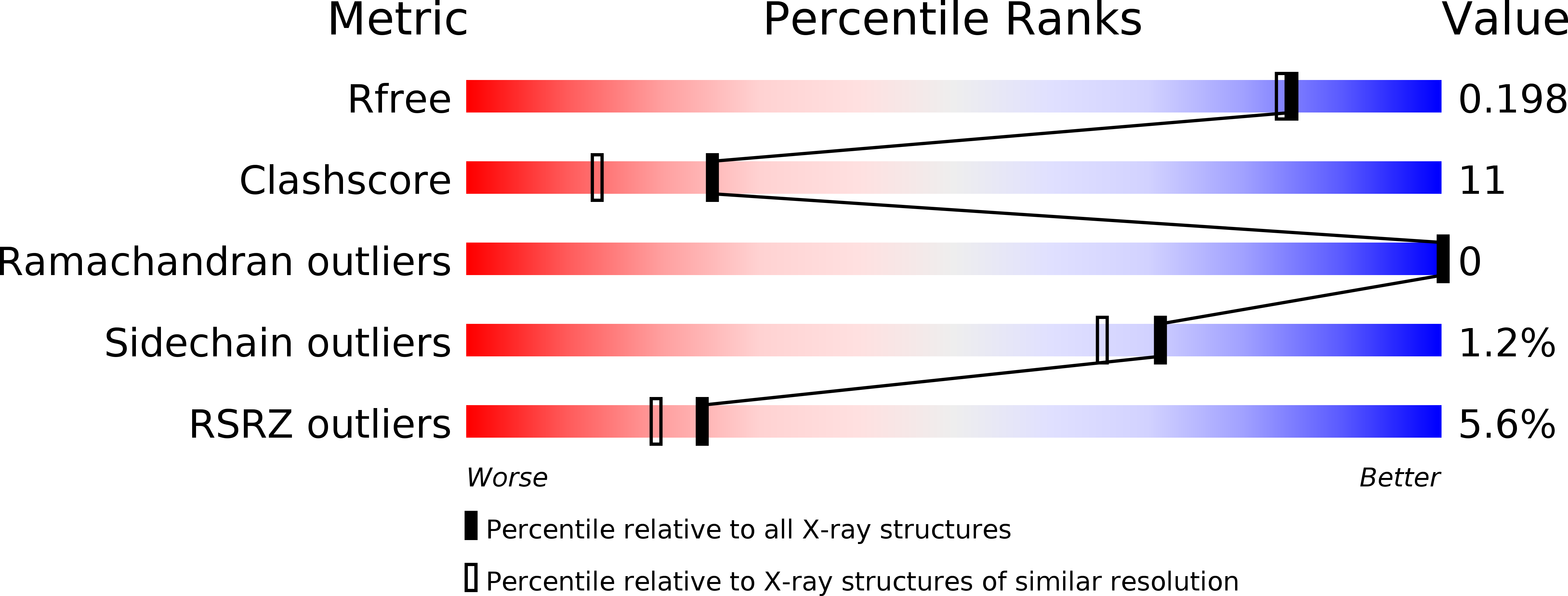
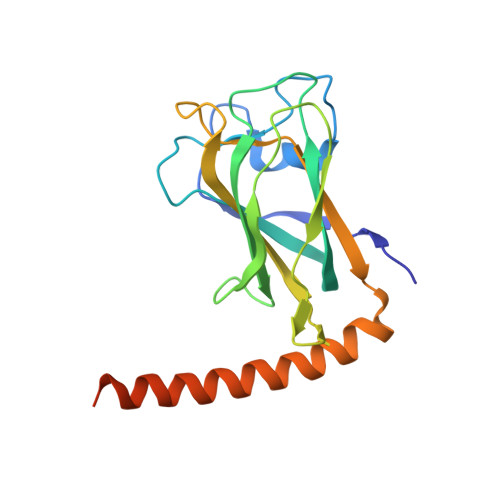
The LisH Motif of Muskelin Is Crucial for Oligomerization and Governs Intracellular Localization.
Delto, C.F., Heisler, F.F., Kuper, J., Sander, B., Kneussel, M., Schindelin, H.(2015) Structure 23: 364-373
- PubMed: 25579817
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2014.11.016
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4OYU - PubMed Abstract:
Neurons regulate the number of surface receptors by balancing the transport to and from the plasma membrane to adjust their signaling properties. The protein muskelin was recently identified as a key factor guiding the transport of α1 subunit-containing GABAA receptors. Here we present the crystal structure of muskelin, comprising its N-terminal discoidin domain and Lis1-homology (LisH) motif. The molecule crystallized as a dimer with the LisH motif exclusively mediating oligomerization. Our subsequent biochemical analyses confirmed that the LisH motif acts as a dimerization element in muskelin. Together with an intermolecular head-to-tail interaction, the LisH-dependent dimerization is required to assemble a muskelin tetramer. Intriguingly, our cellular studies revealed that the loss of this dimerization results in a complete redistribution of muskelin from the cytoplasm to the nucleus and impairs muskelin's function in GABAA receptor transport. These studies demonstrate that the LisH-dependent dimerization is a crucial factor for muskelin function.
Organizational Affiliation:
Rudolf Virchow Center for Experimental Biomedicine, University of Würzburg, D-97080 Würzburg, Germany.