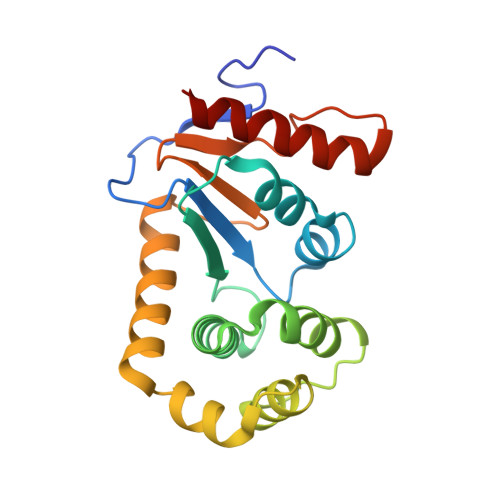
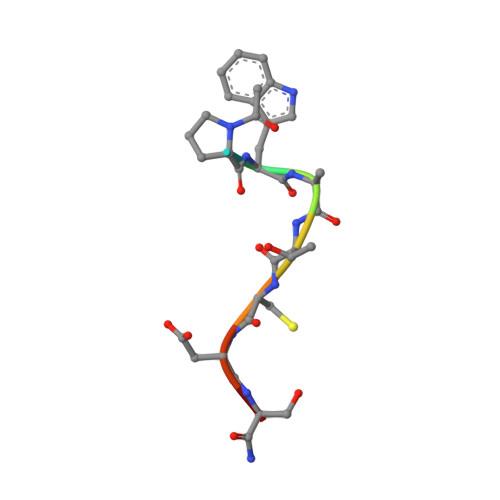
Crystal Structure of the Dithiol Oxidase DsbA Enzyme from Proteus Mirabilis Bound Non-covalently to an Active Site Peptide Ligand.
Kurth, F., Duprez, W., Premkumar, L., Schembri, M.A., Fairlie, D.P., Martin, J.L.(2014) J Biol Chem 289: 19810-19822
- PubMed: 24831013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.552380
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4OCE, 4OCF, 4OD7 - PubMed Abstract:
The disulfide bond forming DsbA enzymes and their DsbB interaction partners are attractive targets for development of antivirulence drugs because both are essential for virulence factor assembly in Gram-negative pathogens. Here we characterize PmDsbA from Proteus mirabilis, a bacterial pathogen increasingly associated with multidrug resistance. PmDsbA exhibits the characteristic properties of a DsbA, including an oxidizing potential, destabilizing disulfide, acidic active site cysteine, and dithiol oxidase catalytic activity. We evaluated a peptide, PWATCDS, derived from the partner protein DsbB and showed by thermal shift and isothermal titration calorimetry that it binds to PmDsbA. The crystal structures of PmDsbA, and the active site variant PmDsbAC30S were determined to high resolution. Analysis of these structures allows categorization of PmDsbA into the DsbA class exemplified by the archetypal Escherichia coli DsbA enzyme. We also present a crystal structure of PmDsbAC30S in complex with the peptide PWATCDS. The structure shows that the peptide binds non-covalently to the active site CXXC motif, the cis-Pro loop, and the hydrophobic groove adjacent to the active site of the enzyme. This high-resolution structural data provides a critical advance for future structure-based design of non-covalent peptidomimetic inhibitors. Such inhibitors would represent an entirely new antibacterial class that work by switching off the DSB virulence assembly machinery.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Institute for Molecular Bioscience, Division of Chemistry and Structural Biology and.