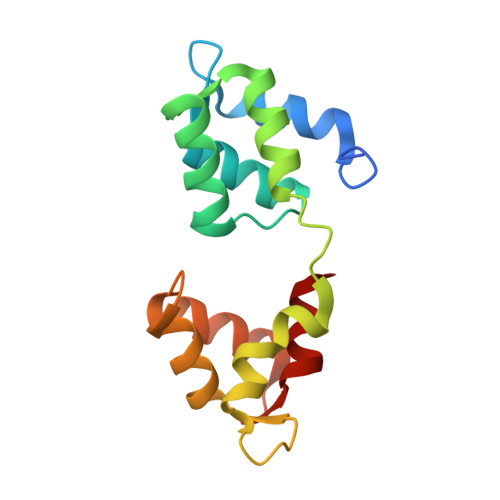
Crystal Structures of Stapled and Hydrogen Bond Surrogate Peptides Targeting a Fully Buried Protein-Helix Interaction.
Douse, C.H., Maas, S.J., Thomas, J.C., Garnett, J.A., Sun, Y., Cota, E., Tate, E.W.(2014) ACS Chem Biol 8: 506-512
- PubMed: 25084543
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/cb500271c
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4MZJ, 4MZK, 4MZL - PubMed Abstract:
Constrained α-helical peptides are an exciting class of molecule designed to disrupt protein-protein interactions (PPIs) at a surface-exposed helix binding site. Complexes that engage more than one helical face account for over a third of structurally characterized helix PPIs, including several examples where the helix is fully buried. However, no constrained peptides have been reported that have targeted this class of interaction. We report the design of stapled and hydrogen bond surrogate (HBS) peptides mimicking the helical tail of the malaria parasite invasion motor myosin (myoA), which presents polar and hydrophobic functionality on all three faces in binding its partner, myoA tail interacting protein (MTIP), with high affinity. The first structures of these different constrained peptides bound to the same target are reported, enabling a direct comparison between these constraints and between staples based on monosubstituted pentenyl glycine (pGly) and disubstituted pentenyl alanine (pAla). Importantly, installation of these constraints does not disrupt native interactions in the buried site, so the affinity of the wild-type peptide is maintained.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, ‡Centre for Structural Biology, Department of Life Sciences, and §Institute of Chemical Biology, Imperial College London , London SW7 2AZ, United Kingdom.