Crystal structure and versatile functional roles of the COP9 signalosome subunit 1.
Lee, J.H., Yi, L., Li, J., Schweitzer, K., Borgmann, M., Naumann, M., Wu, H.(2013) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110: 11845-11850
- PubMed: 23818606
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1302418110
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4LCT - PubMed Abstract:
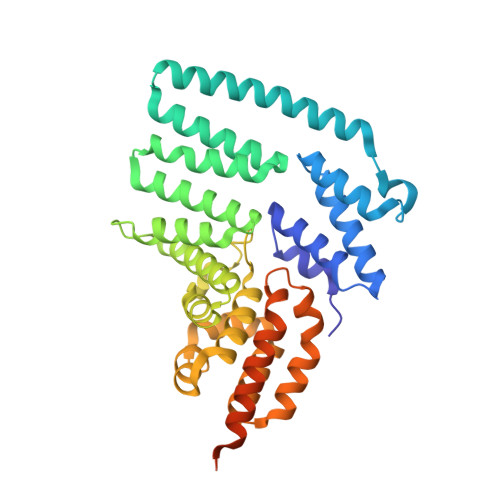
The constitutive photomorphogenesis 9 (COP9) signalosome (CSN) plays key roles in many biological processes, such as repression of photomorphogenesis in plants and protein subcellular localization, DNA-damage response, and NF-κB activation in mammals. It is an evolutionarily conserved eight-protein complex with subunits CSN1 to CSN8 named following the descending order of molecular weights. Here, we report the crystal structure of the largest CSN subunit, CSN1 from Arabidopsis thaliana (atCSN1), which belongs to the Proteasome, COP9 signalosome, Initiation factor 3 (PCI) domain containing CSN subunit family, at 2.7 Å resolution. In contrast to previous predictions and distinct from the PCI-containing 26S proteasome regulatory particle subunit Rpn6 structure, the atCSN1 structure reveals an overall globular fold, with four domains consisting of helical repeat-I, linker helix, helical repeat-II, and the C-terminal PCI domain. Our small-angle X-ray scattering envelope of the CSN1-CSN7 complex agrees with the EM structure of the CSN alone (apo-CSN) and suggests that the PCI end of each molecule may mediate the interaction. Fitting of the CSN1 structure into the CSN-Skp1-Cul1-Fbox (SCF) EM structure shows that the PCI domain of CSN1 situates at the hub of the CSN for interaction with several other subunits whereas the linker helix and helical repeat-II of CSN1 contacts SCF using a conserved surface patch. Furthermore, we show that, in human, the C-terminal tail of CSN1, a segment not included in our crystal structure, interacts with IκBα in the NF-κB pathway. Therefore, the CSN complex uses multiple mechanisms to hinder NF-κB activation, a principle likely to hold true for its regulation of many other targets and pathways.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Weill Cornell Medical College, New York, NY 10065, USA.