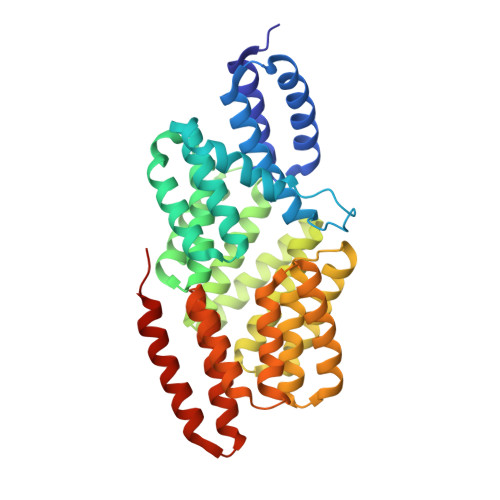
Structural basis of Rap phosphatase inhibition by Phr peptides
Gallego del Sol, F., Marina, A.(2013) PLoS Biol 11: e1001511-e1001511
- PubMed: 23526880
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1001511
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4I9C, 4I9E - PubMed Abstract:
Two-component systems, composed of a sensor histidine kinase and an effector response regulator (RR), are the main signal transduction devices in bacteria. In Bacillus, the Rap protein family modulates complex signaling processes mediated by two-component systems, such as competence, sporulation, or biofilm formation, by inhibiting the RR components involved in these pathways. Despite the high degree of sequence homology, Rap proteins exert their activity by two completely different mechanisms of action: inducing RR dephosphorylation or blocking RR binding to its target promoter. However the regulatory mechanism involving Rap proteins is even more complex since Rap activity is antagonized by specific signaling peptides (Phr) through a mechanism that remains unknown at the molecular level. Using X-ray analyses, we determined the structure of RapF, the anti-activator of competence RR ComA, alone and in complex with its regulatory peptide PhrF. The structural and functional data presented herein reveal that peptide PhrF blocks the RapF-ComA interaction through an allosteric mechanism. PhrF accommodates in the C-terminal tetratricopeptide repeat domain of RapF by inducing its constriction, a conformational change propagated by a pronounced rotation to the N-terminal ComA-binding domain. This movement partially disrupts the ComA binding site by triggering the ComA disassociation, whose interaction with RapF is also sterically impaired in the PhrF-induced conformation of RapF. Sequence analyses of the Rap proteins, guided by the RapF-PhrF structure, unveil the molecular basis of Phr recognition and discrimination, allowing us to relax the Phr specificity of RapF by a single residue change.
Organizational Affiliation:
Instituto de Biomedicina de Valencia, Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, Valencia, Spain.