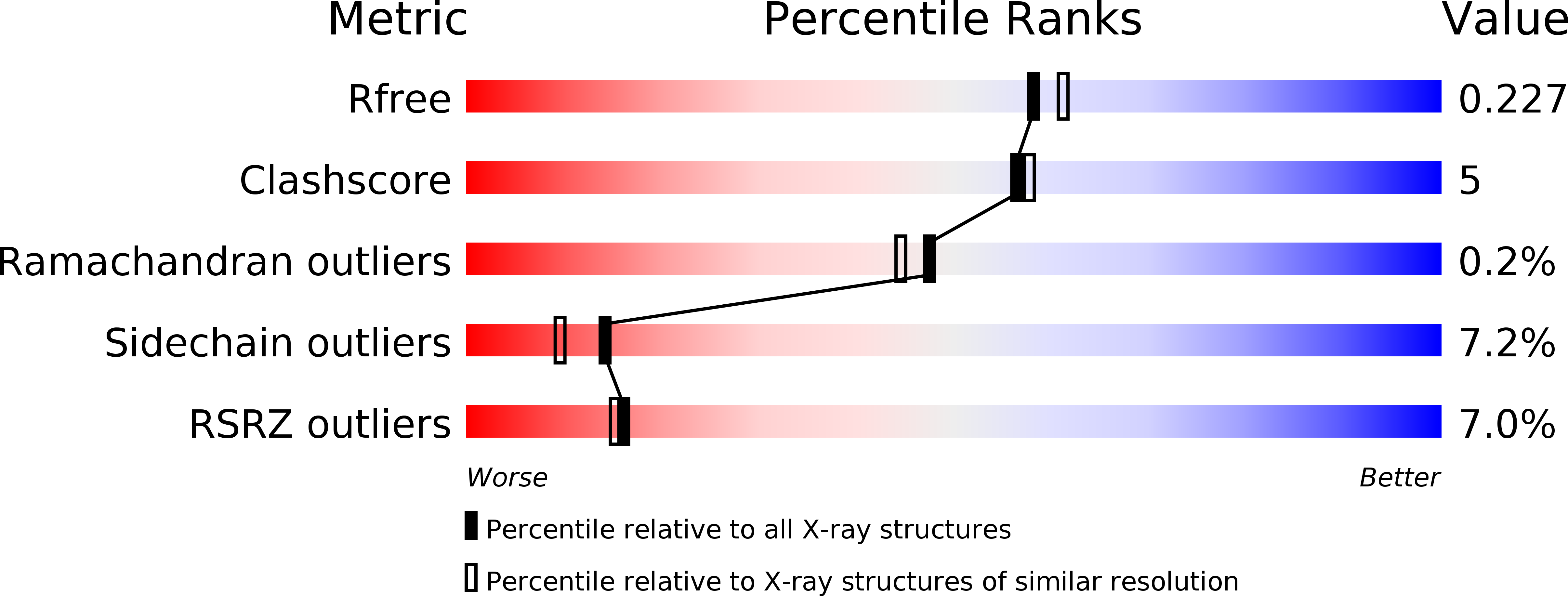
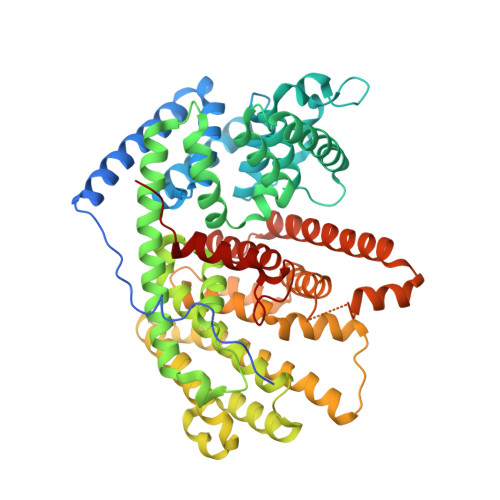
Rational engineering of plasticity residues of sesquiterpene synthases from Artemisia annua: product specificity and catalytic efficiency.
Li, J.X., Fang, X., Zhao, Q., Ruan, J.X., Yang, C.Q., Wang, L.J., Miller, D.J., Faraldos, J.A., Allemann, R.K., Chen, X.Y., Zhang, P.(2013) Biochem J 451: 417-426
- PubMed: 23438177
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20130041
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4FJQ, 4GAX - PubMed Abstract:
Most TPSs (terpene synthases) contain plasticity residues that are responsible for diversified terpene products and functional evolution, which provide a potential for improving catalytic efficiency. Artemisinin, a sesquiterpene lactone from Artemisia annua L., is widely used for malaria treatment and progress has been made in engineering the production of artemisinin or its precursors. In the present paper, we report a new sesquiterpene synthase from A. annua, AaBOS (A. annua α-bisabolol synthase), which has high sequence identity with AaADS (A. annua amorpha-4,11-diene synthase), a key enzyme in artemisinin biosynthesis. Comparative analysis of the two enzymes by domain-swapping and structure-based mutagenesis led to the identification of several plasticity residues, whose alteration changed the product profile of AaBOS to include γ-humulene as the major product. To elucidate the underlying mechanisms, we solved the crystal structures of AaBOS and a γ-humulene-producing AaBOS mutant (termed AaBOS-M2). Among the plasticity residues, position 399, located in the substrate-binding pocket, is crucial for both enzymes. In AaBOS, substitution of threonine for leucine (AaBOSL339T) is required for γ-humulene production; whereas in AaADS, replacing the threonine residue with serine (AaADST399S) resulted in a substantial increase in the activity of amorpha-4,11-diene production, probably as a result of accelerated product release. The present study demonstrates that substitution of plasticity residues has potential for improving catalytic efficiency of the enzyme.
Organizational Affiliation:
National Key Laboratory of Plant Molecular Genetics and National Plant Gene Research Center, Institute of Plant Physiology and Ecology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 300 Fenglin Road, Shanghai 200032, China.