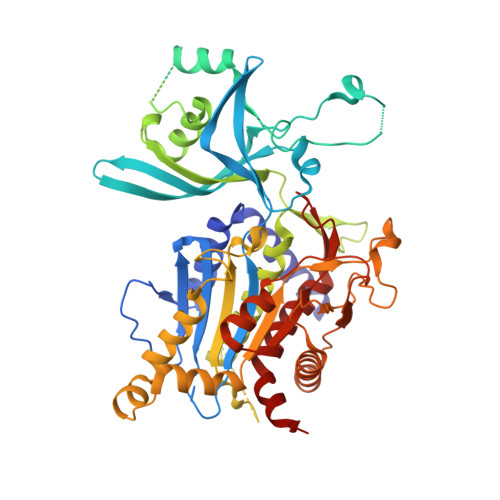
X-ray crystal structure and specificity of the Plasmodium falciparum malaria aminopeptidase PfM18AAP.
Sivaraman, K.K., Oellig, C.A., Huynh, K., Atkinson, S.C., Poreba, M., Perugini, M.A., Trenholme, K.R., Gardiner, D.L., Salvesen, G., Drag, M., Dalton, J.P., Whisstock, J.C., McGowan, S.(2012) J Mol Biol 422: 495-507
- PubMed: 22709581
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2012.06.006
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4EME - PubMed Abstract:
The malarial aminopeptidases have emerged as promising new drug targets for the development of novel antimalarial drugs. The M18AAP of Plasmodium falciparum malaria is a metallo-aminopeptidase that we show demonstrates a highly restricted specificity for peptides with an N-terminal Glu or Asp residue. Thus, the enzyme may function alongside other aminopeptidases in effecting the complete degradation or turnover of proteins, such as host hemoglobin, which provides a free amino acid pool for the growing parasite. Inhibition of PfM18AAP's function using antisense RNA is detrimental to the intra-erythrocytic malaria parasite and, hence, it has been proposed as a potential novel drug target. We report the X-ray crystal structure of the PfM18AAP aminopeptidase and reveal its complex dodecameric assembly arranged via dimer and trimer units that interact to form a large tetrahedron shape that completely encloses the 12 active sites within a central cavity. The four entry points to the catalytic lumen are each guarded by 12 large flexible loops that could control substrate entry into the catalytic sites. PfM18AAP thus resembles a proteasomal-like machine with multiple active sites able to degrade peptide substrates that enter the central lumen. The Plasmodium enzyme shows significant structural differences around the active site when compared to recently determined structures of its mammalian and human homologs, which provides a platform from which a rational approach to inhibitor design of new malaria-specific drugs can begin.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Monash University, Clayton Campus, Melbourne, VIC 3800, Australia.