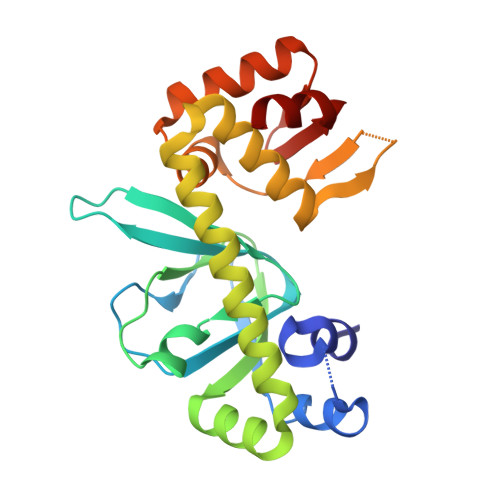
The Crystal Structures of Apo and Camp-Bound Glxr from Corynebacterium Glutamicum Reveal Structural and Dynamic Changes Upon Camp Binding in Crp/Fnr Family Transcription Factors.
Townsend, P.D., Jungwirth, B., Pojer, F., Bussmann, M., Money, V.A., Cole, S.T., Puhler, A., Tauch, A., Bott, M., Cann, M.J., Pohl, E.(2014) PLoS One 9: 3265
- PubMed: 25469635
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0113265
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4BYY, 4CYD - PubMed Abstract:
The cyclic AMP-dependent transcriptional regulator GlxR from Corynebacterium glutamicum is a member of the super-family of CRP/FNR (cyclic AMP receptor protein/fumarate and nitrate reduction regulator) transcriptional regulators that play central roles in bacterial metabolic regulatory networks. In C. glutamicum, which is widely used for the industrial production of amino acids and serves as a non-pathogenic model organism for members of the Corynebacteriales including Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the GlxR homodimer controls the transcription of a large number of genes involved in carbon metabolism. GlxR therefore represents a key target for understanding the regulation and coordination of C. glutamicum metabolism. Here we investigate cylic AMP and DNA binding of GlxR from C. glutamicum and describe the crystal structures of apo GlxR determined at a resolution of 2.5 Å, and two crystal forms of holo GlxR at resolutions of 2.38 and 1.82 Å, respectively. The detailed structural analysis and comparison of GlxR with CRP reveals that the protein undergoes a distinctive conformational change upon cyclic AMP binding leading to a dimer structure more compatible to DNA-binding. As the two binding sites in the GlxR homodimer are structurally identical dynamic changes upon binding of the first ligand are responsible for the allosteric behavior. The results presented here show how dynamic and structural changes in GlxR lead to optimization of orientation and distance of its two DNA-binding helices for optimal DNA recognition.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Biological and Biomedical Sciences & Department of Chemistry, Biophysical Sciences Institute, Durham University, Durham, United Kingdom.