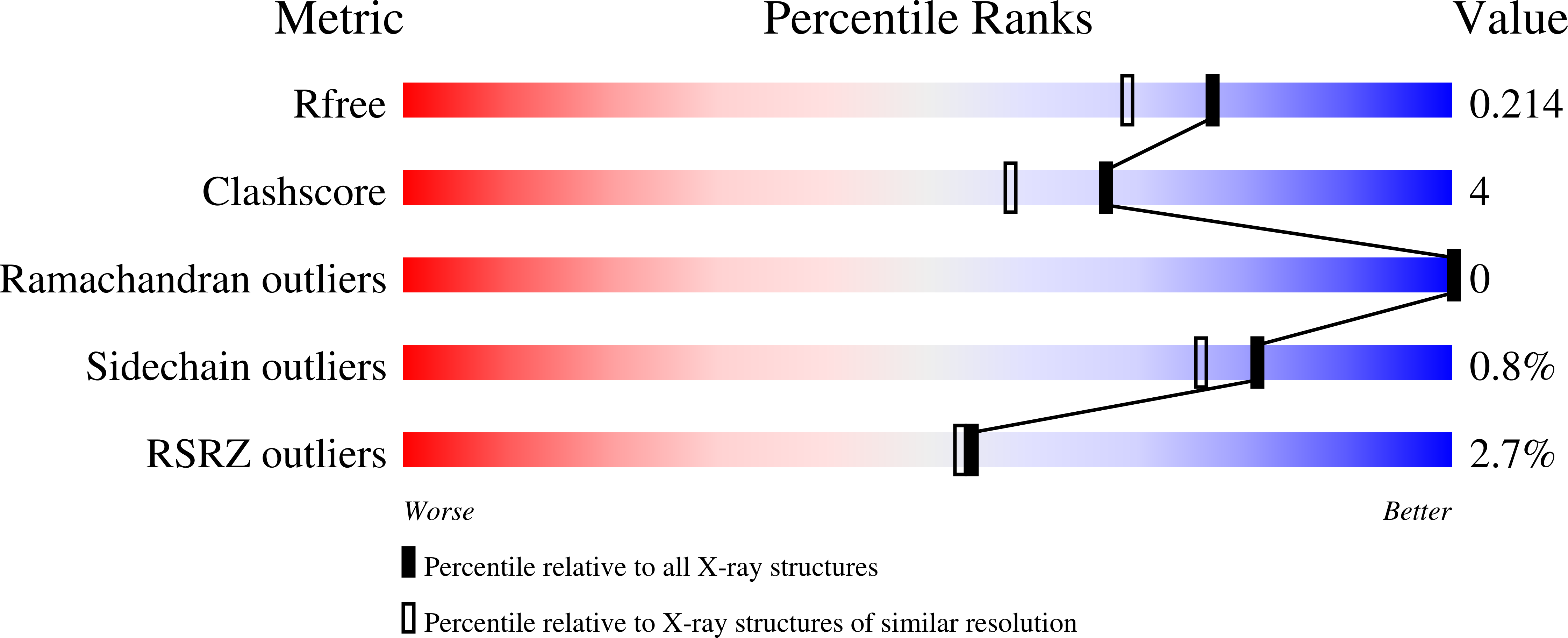
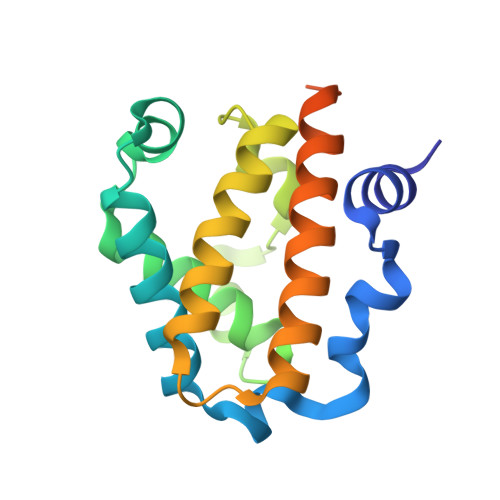
The Structure of a Class 3 Nonsymbiotic Plant Haemoglobin from Arabidopsis Thaliana Reveals a Novel N-Terminal Helical Extension
Reeder, B.J., Hough, M.A.(2014) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 70: 1411
- PubMed: 24816109
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S1399004714004878
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4C0N - PubMed Abstract:
Plant nonsymbiotic haemoglobins fall into three classes, each with distinct properties but all with largely unresolved physiological functions. Here, the first crystal structure of a class 3 nonsymbiotic plant haemoglobin, that from Arabidopsis thaliana, is reported to 1.77 Å resolution. The protein forms a homodimer, with each monomer containing a two-over-two α-helical domain similar to that observed in bacterial truncated haemoglobins. A novel N-terminal extension comprising two α-helices plays a major role in the dimer interface, which occupies the periphery of the dimer-dimer face, surrounding an open central cavity. The haem pocket contains a proximal histidine ligand and an open sixth iron-coordination site with potential for a ligand, in this structure hydroxide, to form hydrogen bonds to a tyrosine or a tryptophan residue. The haem pocket appears to be unusually open to the external environment, with another cavity spanning the entrance of the two haem pockets. The final 23 residues of the C-terminal domain are disordered in the structure; however, these domains in the functional dimer are adjacent and include the only two cysteine residues in the protein sequence. It is likely that these residues form disulfide bonds in vitro and it is conceivable that this C-terminal region may act in a putative complex with a partner molecule in vivo.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Biological Sciences, University of Essex, Wivenhoe Park, Colchester, Essex CO4 3SQ, England.