The Impact of Nitration on the Structure and Immunogenicity of the Major Birch Pollen Allergen Bet V 1.0101.
Ackaert, C., Kofler, S., Horejs-Hoeck, J., Zulehner, N., Asam, C., Von Grafenstein, S., Fuchs, J.E., Briza, P., Liedl, K.R., Bohle, B., Ferreira, F., Brandstetter, H., Oostingh, G.J., Duschl, A.(2014) PLoS One 9: 4520
- PubMed: 25126882
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0104520
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
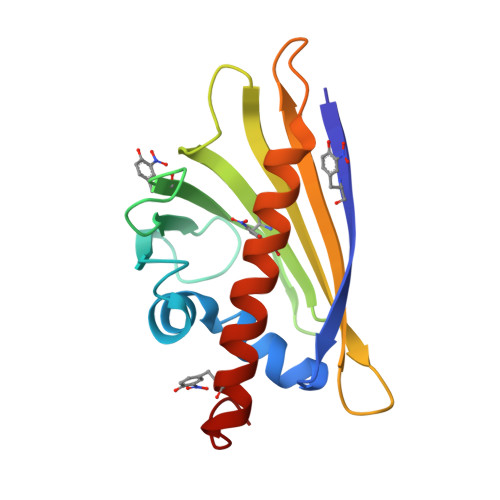
4B9R - PubMed Abstract:
Allergy prevalence has increased in industrialized countries. One contributing factor could be pollution, which can cause nitration of allergens exogenously (in the air) or endogenously (in inflamed lung tissue). We investigated the impact of nitration on both the structural and immunological behavior of the major birch pollen allergen Bet v 1.0101 to determine whether nitration might be a factor in the increased incidence of allergy. Bet v 1.0101 was nitrated with tetranitromethane. Immune effects were assessed by measuring the proliferation of specific T-cell lines (TCLs) upon stimulation with different concentrations of nitrated and unmodified allergen, and by measurement of cytokine release of monocyte-derived dendritic cells (moDCs) and primary DCs (primDCs) stimulated with nitrated versus unmodified allergen. HPLC-MS, crystallography, gel electrophoresis, amino acid analysis, size exclusion chromatography and molecular dynamics simulation were performed to characterize structural changes after nitration of the allergen. The proliferation of specific TCLs was higher upon stimulation with the nitrated allergen in comparison to the unmodified allergen. An important structural consequence of nitration was oligomerization. Moreover, analysis of the crystal structure of nitrated Bet v 1.0101 showed that amino acid residue Y83, located in the hydrophobic cavity, was nitrated to 100%. Both moDCs and primDCs showed decreased production of TH1-priming cytokines, thus favoring a TH2 response. These results implicate that nitration of Bet v 1.0101 might be a contributing factor to the observed increase in birch pollen allergy, and emphasize the importance of protein modifications in understanding the molecular basis of allergenicity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Biology, University of Salzburg, Salzburg, Austria.