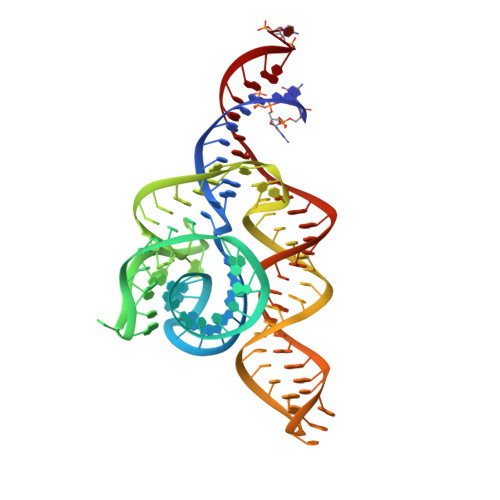
Structure of the complete bacterial SRP Alu domain.
Kempf, G., Wild, K., Sinning, I.(2014) Nucleic Acids Res 42: 12284-12294
- PubMed: 25270875
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku883
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4WFL, 4WFM - PubMed Abstract:
The Alu domain of the signal recognition particle (SRP) arrests protein biosynthesis by competition with elongation factor binding on the ribosome. The mammalian Alu domain is a protein-RNA complex, while prokaryotic Alu domains are protein-free with significant extensions of the RNA. Here we report the crystal structure of the complete Alu domain of Bacillus subtilis SRP RNA at 2.5 Å resolution. The bacterial Alu RNA reveals a compact fold, which is stabilized by prokaryote-specific extensions and interactions. In this 'closed' conformation, the 5' and 3' regions are clamped together by the additional helix 1, the connecting 3-way junction and a novel minor groove interaction, which we term the 'minor-saddle motif' (MSM). The 5' region includes an extended loop-loop pseudoknot made of five consecutive Watson-Crick base pairs. Homology modeling with the human Alu domain in context of the ribosome shows that an additional lobe in the pseudoknot approaches the large subunit, while the absence of protein results in the detachment from the small subunit. Our findings provide the structural basis for purely RNA-driven elongation arrest in prokaryotes, and give insights into the structural adaption of SRP RNA during evolution.
Organizational Affiliation:
Heidelberg University Biochemistry Center (BZH), INF 328, D-69120 Heidelberg, Germany.