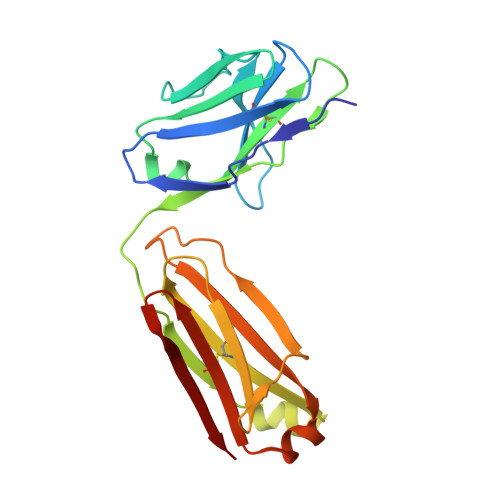
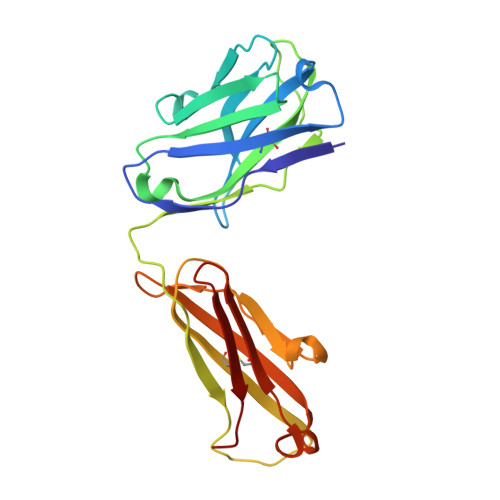
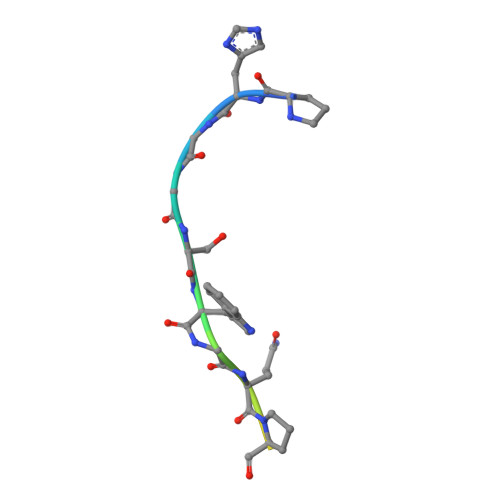
The crystal structure of an octapeptide repeat of the Prion protein in complex with a Fab fragment of the POM2 antibody.
Swayampakula, M., Baral, P.K., Aguzzi, A., Kav, N.N., James, M.N.(2013) Protein Sci 22: 893-903
- PubMed: 23629842
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.2270
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4J8R - PubMed Abstract:
Prion diseases are progressive, infectious neurodegenerative disorders caused primarily by the misfolding of the cellular prion protein (PrP(c)) into an insoluble, protease-resistant, aggregated isoform termed PrP(sc). In native conditions, PrP(c) has a structured C-terminal domain and a highly flexible N-terminal domain. A part of this N-terminal domain consists of 4-5 repeats of an unusual glycine-rich, eight amino acids long peptide known as the octapeptide repeat (OR) domain. In this article, we successfully report the first crystal structure of an OR of PrP(c) bound to the Fab fragment of the POM2 antibody. The structure was solved at a resolution of 2.3 Å by molecular replacement. Although several studies have previously predicted a β-turn-like structure of the unbound ORs, our structure shows an extended conformation of the OR when bound to a molecule of the POM2 Fab indicating that the bound Fab disrupts any putative native β turn conformation of the ORs. Encouraging results from several recent studies have shown that administering small molecule ligands or antibodies targeting the OR domain of PrP result in arresting the progress of peripheral prion infections both in ex vivo and in in vivo models. This makes the structural study of the interactions of POM2 Fab with the OR domain very important as it would help us to design smaller and tighter binding OR ligands.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, T6G 2H7, Canada.