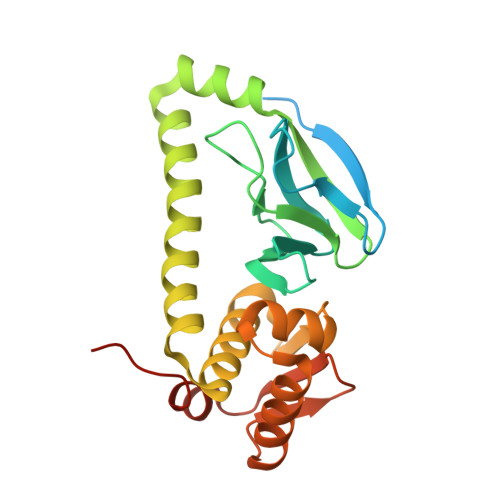
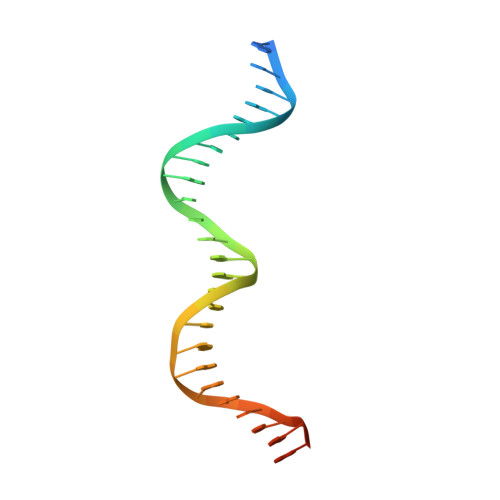
The Structure of Bradyrhizobium japonicum Transcription Factor FixK2 Unveils Sites of DNA Binding and Oxidation.
Bonnet, M., Kurz, M., Mesa, S., Briand, C., Hennecke, H., Grutter, M.G.(2013) J Biol Chem 288: 14238-14246
- PubMed: 23546876
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.465484
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4I2O - PubMed Abstract:
FixK2 is a regulatory protein that activates a large number of genes for the anoxic and microoxic, endosymbiotic, and nitrogen-fixing life styles of the α-proteobacterium Bradyrhizobium japonicum. FixK2 belongs to the cAMP receptor protein (CRP) superfamily. Although most CRP family members are coregulated by effector molecules, the activity of FixK2 is negatively controlled by oxidation of its single cysteine (Cys-183) located next to the DNA-binding domain and possibly also by proteolysis. Here, we report the three-dimensional x-ray structure of FixK2, a representative of the FixK subgroup of the CRP superfamily. Crystallization succeeded only when (i) an oxidation- and protease-insensitive protein variant (FixK2(C183S)-His6) was used in which Cys-183 was replaced with serine and the C terminus was fused with a hexahistidine tag and (ii) this protein was allowed to form a complex with a 30-mer double-stranded target DNA. The structure of the FixK2-DNA complex was solved at a resolution of 1.77 Å, at which the protein formed a homodimer. The precise protein-DNA contacts were identified, which led to an affirmation of the canonical target sequence, the so-called FixK2 box. The C terminus is surface-exposed, which might explain its sensitivity to specific cleavage and degradation. The oxidation-sensitive Cys-183 is also surface-exposed and in close proximity to DNA. Therefore, we propose a mechanism whereby the oxo acids generated after oxidation of the cysteine thiol cause an electrostatic repulsion, thus preventing specific DNA binding.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Microbiology, Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule (ETH), CH-8093 Zürich, Switzerland.