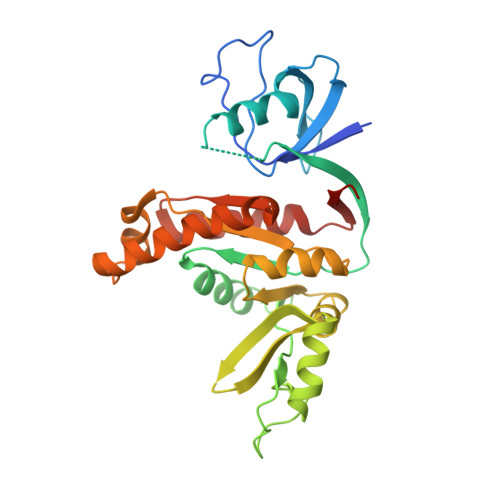
Guanylate kinase domains of the MAGUK family scaffold proteins as specific phospho-protein-binding modules
Zhu, J., Shang, Y., Xia, C., Wang, W., Wen, W., Zhang, M.(2011) EMBO J
- PubMed: 22117215
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2011.428
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3UAT - PubMed Abstract:
Membrane-associated guanylate kinases (MAGUKs) are a large family of scaffold proteins that play essential roles in tissue developments, cell-cell communications, cell polarity control, and cellular signal transductions. Despite extensive studies over the past two decades, the functions of the signature guanylate kinase domain (GK) of MAGUKs are poorly understood. Here we show that the GK domain of DLG1/SAP97 binds to asymmetric cell division regulatory protein LGN in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. The structure of the DLG1 SH3-GK tandem in complex with a phospho-LGN peptide reveals that the GMP-binding site of GK has evolved into a specific pSer/pThr-binding pocket. Residues both N- and C-terminal to the pSer are also critical for the specific binding of the phospho-LGN peptide to GK. We further demonstrate that the previously reported GK domain-mediated interactions of DLGs with other targets, such as GKAP/DLGAP1/SAPAP1 and SPAR, are also phosphorylation dependent. Finally, we provide evidence that other MAGUK GKs also function as phospho-peptide-binding modules. The discovery of the phosphorylation-dependent MAGUK GK/target interactions indicates that MAGUK scaffold-mediated signalling complex organizations are dynamically regulated.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, and Institutes of Biomedical Sciences, Fudan University, Shanghai, PR China.