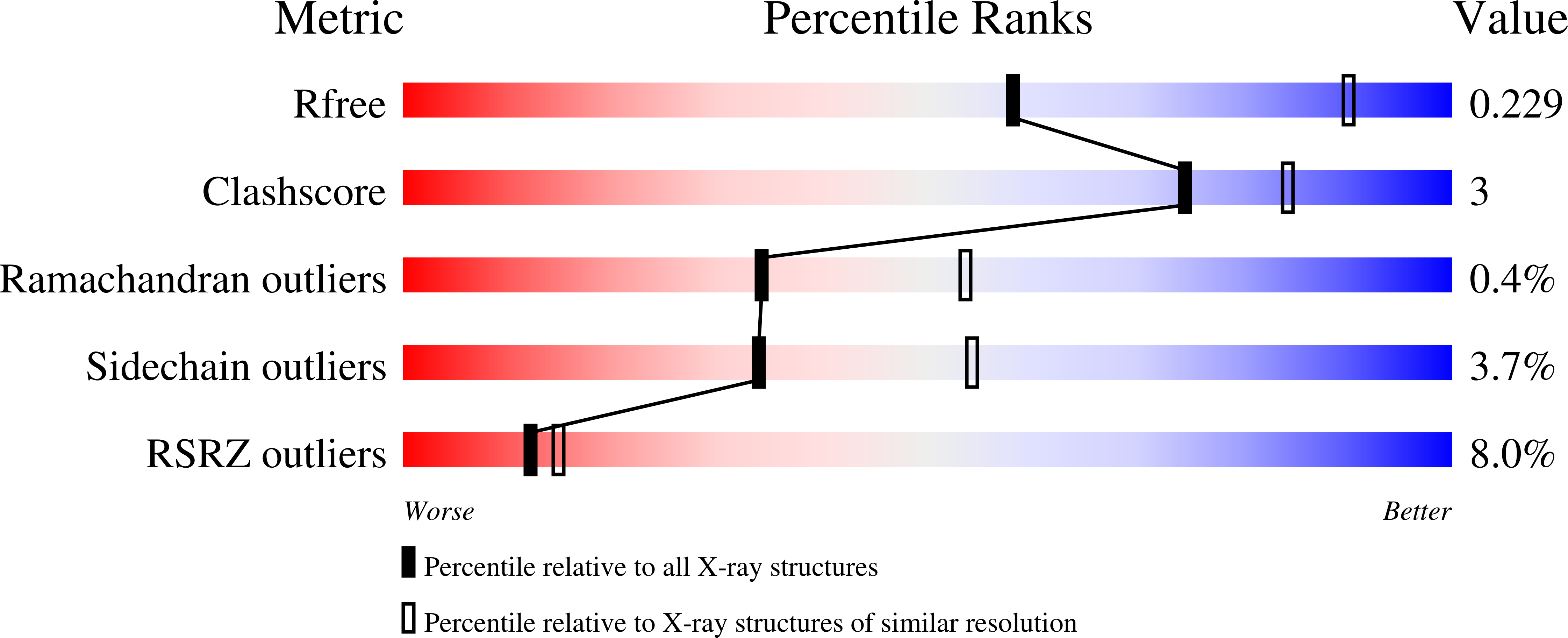
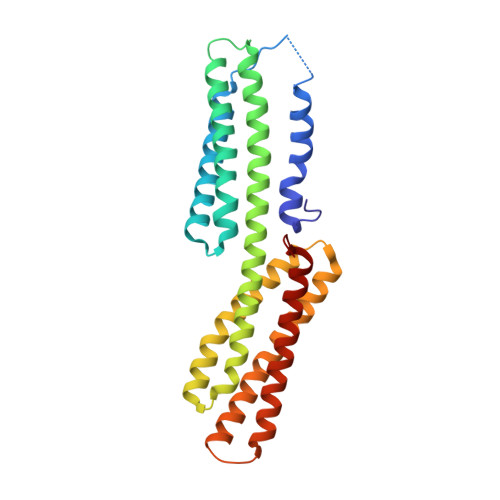
The rickettsia surface cell antigen 4 applies mimicry to bind to and activate vinculin.
Park, H., Lee, J.H., Gouin, E., Cossart, P., Izard, T.(2011) J Biol Chem 286: 35096-35103
- PubMed: 21841197
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.263855
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3TJ5, 3TJ6 - PubMed Abstract:
Pathogenic Rickettsia species cause high morbidity and mortality, especially R. prowazekii, the causative agent of typhus. Like many intracellular pathogens, Rickettsia exploit the cytoskeleton to enter and spread within the host cell. Here we report that the cell surface antigen sca4 of Rickettsia co-localizes with vinculin in cells at sites of focal adhesions in sca4-transfected cells and that sca4 binds to and activates vinculin through two vinculin binding sites (VBSs) that are conserved across all Rickettsia. Remarkably, this occurs through molecular mimicry of the vinculin-talin interaction that is also seen with the IpaA invasin of the intracellular pathogen Shigella, where binding of these VBSs to the vinculin seven-helix bundle head domain (Vh1) displaces intramolecular interactions with the vinculin tail domain that normally clamp vinculin in an inactive state. Finally, the vinculin·sca4-VBS crystal structures reveal that vinculin adopts a new conformation when bound to the C-terminal VBS of sca4. Collectively, our data define the mechanism by which sca4 activates vinculin and interacts with the actin cytoskeleton, and they suggest important roles for vinculin in Rickettsia pathogenesis.
Organizational Affiliation:
Cell Adhesion Laboratory, Department of Cancer Biology, The Scripps Research Institute, Jupiter, Florida 33458, USA.