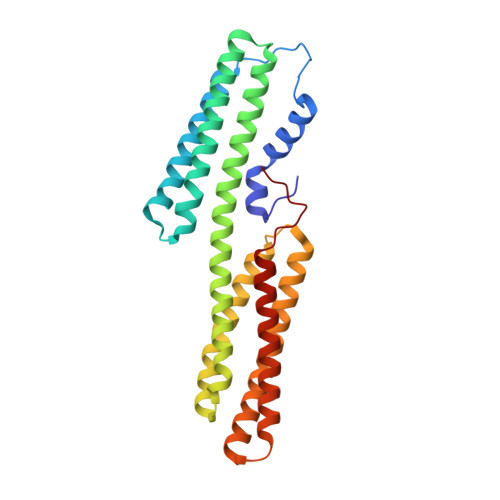
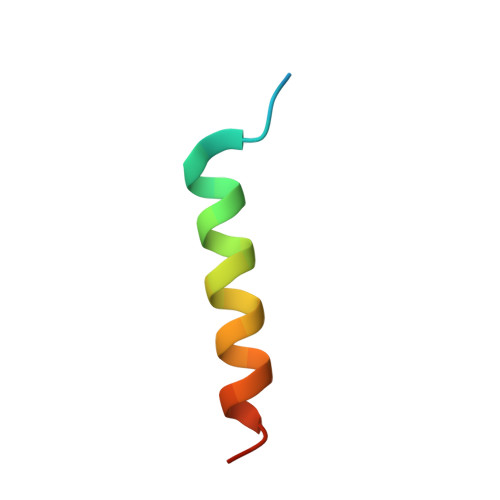
Novel vinculin binding site of the IpaA invasin of Shigella.
Park, H., Valencia-Gallardo, C., Sharff, A., Tran Van Nhieu, G., Izard, T.(2011) J Biol Chem 286: 23214-23221
- PubMed: 21525010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.184283
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3RF3 - PubMed Abstract:
Internalization of Shigella into host epithelial cells, where the bacteria replicates and spreads to neighboring cells, requires a type 3 secretion system (T3SS) effector coined IpaA. IpaA binds directly to and activates the cytoskeletal protein vinculin after injection in the host cell cytosol, and this was previously thought to be directed by two amphipathic α-helical vinculin-binding sites (VBS) found in the C-terminal tail domain of IpaA. Here, we report a third VBS, IpaA-VBS3, that is located N-terminal to the other two VBSs of IpaA and show that one IpaA molecule can bind up to three vinculin molecules. Biochemical in vitro Shigella invasion assays and the 1.6 Å crystal structure of the vinculin·IpaA-VBS3 complex showed that IpaA-VBS3 is functionally redundant with the other two IpaA-VBSs in cell invasion and in activating the latent F-actin binding functions of vinculin. Multiple VBSs in IpaA are reminiscent of talin, which harbors 11 VBSs. However, most of the talin VBSs have low affinity and are buried in helix bundles, whereas all three of the VBSs of IpaA are high affinity, readily available, and in close proximity to each other in the IpaA structure. Although deletion of IpaA-VBS3 has no detectable effects on Shigella invasion of epithelial cells, deletion of all three VBSs impaired bacterial invasion to levels found in an ipaA null mutant strain. Thus, IpaA-directed mimicry of talin in activating vinculin occurs through three high affinity VBSs that are essential for Shigella pathogenesis.
Organizational Affiliation:
Cell Adhesion Laboratory, Department of Cancer Biology, Scripps Research Institute, Jupiter, Florida 33458, USA.