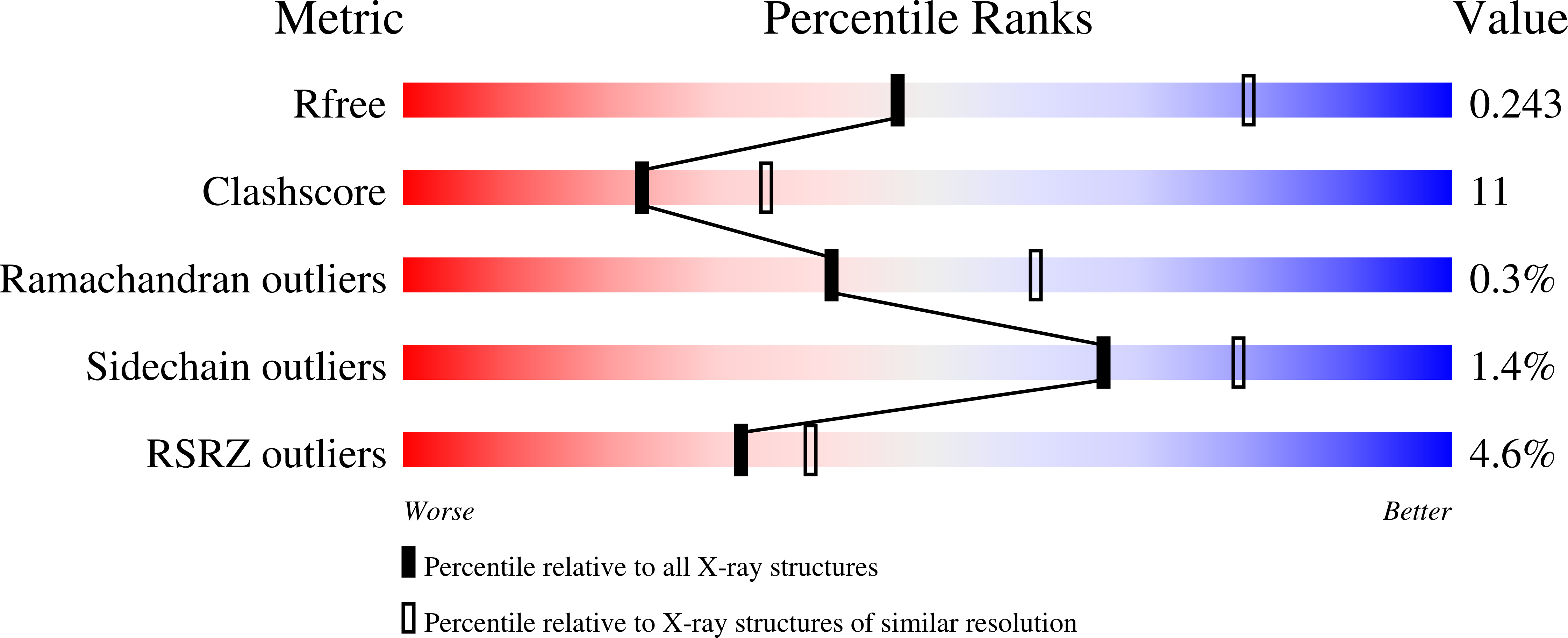
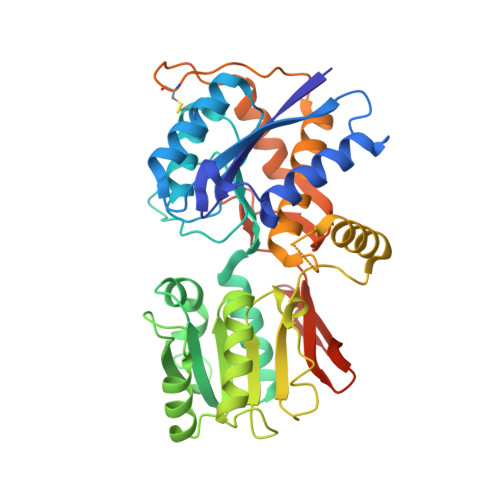
Crystal Structures of the Glutamate Receptor Ion Channel GluK3 and GluK5 Amino-Terminal Domains.
Kumar, J., Mayer, M.L.(2010) J Mol Biol 404: 680-696
- PubMed: 20951142
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2010.10.006
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3OLZ, 3OM0, 3OM1 - PubMed Abstract:
Ionotropic glutamate receptors (iGluRs) mediate the majority of fast excitatory synaptic neurotransmission in the central nervous system. The selective assembly of iGluRs into AMPA, kainate, and N-methyl-d-aspartic acid (NMDA) receptor subtypes is regulated by their extracellular amino-terminal domains (ATDs). Kainate receptors are further classified into low-affinity receptor families (GluK1-GluK3) and high-affinity receptor families (GluK4-GluK5) based on their affinity for the neurotoxin kainic acid. These two families share a 42% sequence identity for the intact receptor but only a 27% sequence identity at the level of ATD. We have determined for the first time the high-resolution crystal structures of GluK3 and GluK5 ATDs, both of which crystallize as dimers but with a strikingly different dimer assembly at the R1 interface. By contrast, for both GluK3 and GluK5, the R2 domain dimer assembly is similar to those reported previously for other non-NMDA iGluRs. This observation is consistent with the reports that GluK4-GluK5 cannot form functional homomeric ion channels and require obligate coassembly with GluK1-GluK3. Our analysis also reveals that the relative orientation of domains R1 and R2 in individual non-NMDA receptor ATDs varies by up to 10°, in contrast to the 50° difference reported for the NMDA receptor GluN2B subunit. This restricted domain movement in non-NMDA receptor ATDs seems to result both from extensive intramolecular contacts between domain R1 and domain R2 and from their assembly as dimers, which interact at both R1 and R2 domains. Our results provide the first insights into the structure and function of GluK4-GluK5, the least understood family of iGluRs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Cellular and Molecular Neurophysiology, Porter Neuroscience Research Center, National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD 20892, USA.