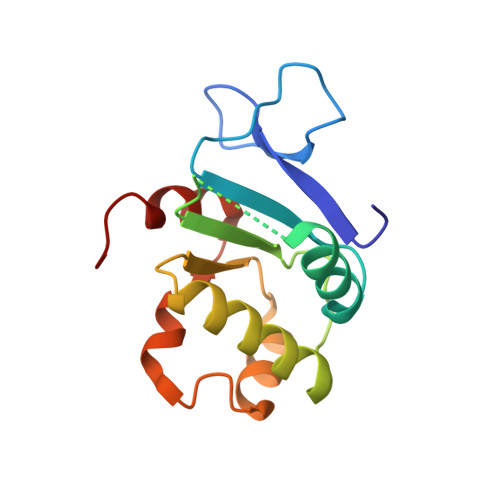
Structure of the cytosolic portion of the motor protein prestin and functional role of the STAS domain in SLC26/SulP anion transporters.
Pasqualetto, E., Aiello, R., Gesiot, L., Bonetto, G., Bellanda, M., Battistutta, R.(2010) J Mol Biol 400: 448-462
- PubMed: 20471983
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2010.05.013
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3LLO - PubMed Abstract:
Prestin is the motor protein responsible for the somatic electromotility of cochlear outer hair cells and is essential for normal hearing sensitivity and frequency selectivity of mammals. Prestin is a member of mammalian solute-linked carrier 26 (SLC26) anion exchangers, a family of membrane proteins capable of transporting a wide variety of monovalent and divalent anions. SLC26 transporters play important roles in normal human physiology in different tissues, and many of them are involved in genetic diseases. SLC26 and related SulP transporters carry a hydrophobic membrane core and a C-terminal cytosolic portion that is essential in plasma membrane targeting and protein function. This C-terminal portion is mainly composed of a STAS (sulfate transporters and anti-sigma factor antagonist) domain, whose name is due to a remote but significant sequence similarity with bacterial ASA (anti-sigma factor antagonist) proteins. Here we present the crystal structure at 1.57 A resolution of the cytosolic portion of prestin, the first structure of a SulP transporter STAS domain, and its characterization in solution by heteronuclear multidimensional NMR spectroscopy. Prestin STAS significantly deviates from the related bacterial ASA proteins, especially in the N-terminal region, which-although previously considered merely as a generic linker between the domain and the last transmembrane helix-is indeed fully part of the domain. Hence, unexpectedly, our data reveal that the STAS domain starts immediately after the last transmembrane segment and lies beneath the lipid bilayer. A structure-function analysis suggests that this model can be a general template for most SLC26 and SulP anion transporters and supports the notion that STAS domains are involved in functionally important intramolecular and intermolecular interactions. Mapping of disease-associated or functionally harmful mutations on STAS structure indicates that they can be divided into two categories: those causing significant misfolding of the domain and those altering its interaction properties.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemical Sciences, University of Padua, via Marzolo 1, 35131 Padua, Italy.