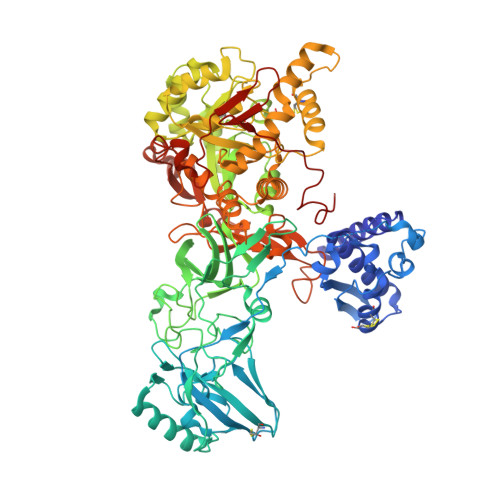
Crystal structure of the first plant urease from jack bean: 83 years of journey from its first crystal to molecular structure
Balasubramanian, A., Ponnuraj, K.(2010) J Mol Biol 400: 274-283
- PubMed: 20471401
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2010.05.009
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3LA4 - PubMed Abstract:
Urease, a nickel-dependent metalloenzyme, is synthesized by plants, some bacteria, and fungi. It catalyzes the hydrolysis of urea into ammonia and carbon dioxide. Although the amino acid sequences of plant and bacterial ureases are closely related, some biological activities differ significantly. Plant ureases but not bacterial ureases possess insecticidal properties independent of its ureolytic activity. To date, the structural information is available only for bacterial ureases although the jack bean urease (Canavalia ensiformis; JBU), the best-studied plant urease, was the first enzyme to be crystallized in 1926. To better understand the biological properties of plant ureases including the mechanism of insecticidal activity, we initiated the structural studies on some of them. Here, we report the crystal structure of JBU, the first plant urease structure, at 2.05 A resolution. The active-site architecture of JBU is similar to that of bacterial ureases containing a bi-nickel center. JBU has a bound phosphate and covalently modified residue (Cys592) by beta-mercaptoethanol at its active site, and the concomitant binding of multiple inhibitors (phosphate and beta-mercaptoethanol) is not observed so far in bacterial ureases. By correlating the structural information of JBU with the available biophysical and biochemical data on insecticidal properties of plant ureases, we hypothesize that the amphipathic beta-hairpin located in the entomotoxic peptide region of plant ureases might form a membrane insertion beta-barrel as found in beta-pore-forming toxins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Centre of Advanced Study in Crystallography and Biophysics, University of Madras, Guindy Campus, Chennai 600 025, India.