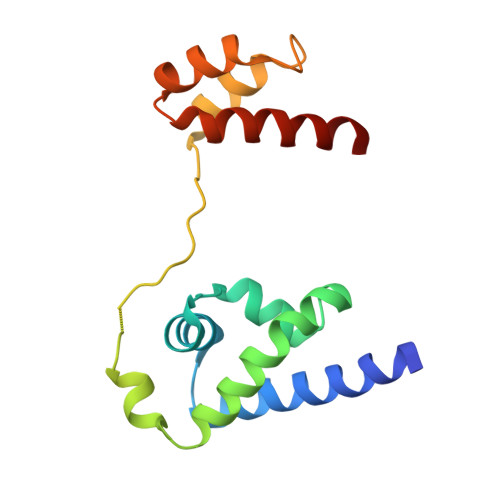
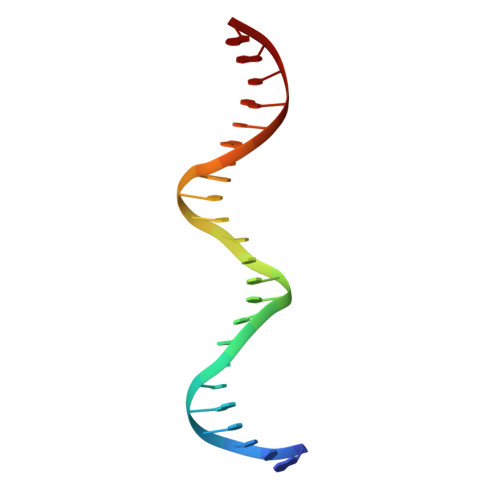
A unique Oct4 interface is crucial for reprogramming to pluripotency
Esch, D., Vahokoski, J., Groves, M.R., Pogenberg, V., Cojocaru, V., Vom Bruch, H., Han, D., Drexler, H.C.A., Arauzo-Bravo, M.J., Ng, C.K.L., Jauch, R., Wilmanns, M., Scholer, H.R.(2013) Nat Cell Biol 15: 295-301
- PubMed: 23376973
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2680
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3L1P - PubMed Abstract:
Terminally differentiated cells can be reprogrammed to pluripotency by the forced expression of Oct4, Sox2, Klf4 and c-Myc. However, it remains unknown how this leads to the multitude of epigenetic changes observed during the reprogramming process. Interestingly, Oct4 is the only factor that cannot be replaced by other members of the same family to induce pluripotency. To understand the unique role of Oct4 in reprogramming, we determined the structure of its POU domain bound to DNA. We show that the linker between the two DNA-binding domains is structured as an α-helix and exposed to the protein's surface, in contrast to the unstructured linker of Oct1. Point mutations in this α-helix alter or abolish the reprogramming activity of Oct4, but do not affect its other fundamental properties. On the basis of mass spectrometry studies of the interactome of wild-type and mutant Oct4, we propose that the linker functions as a protein-protein interaction interface and plays a crucial role during reprogramming by recruiting key epigenetic players to Oct4 target genes. Thus, we provide molecular insights to explain how Oct4 contributes to the reprogramming process.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department for Cell and Developmental Biology, Max Planck Institute for Molecular Biomedicine, Röntgenstrasse 20, Münster D-48149, Germany.