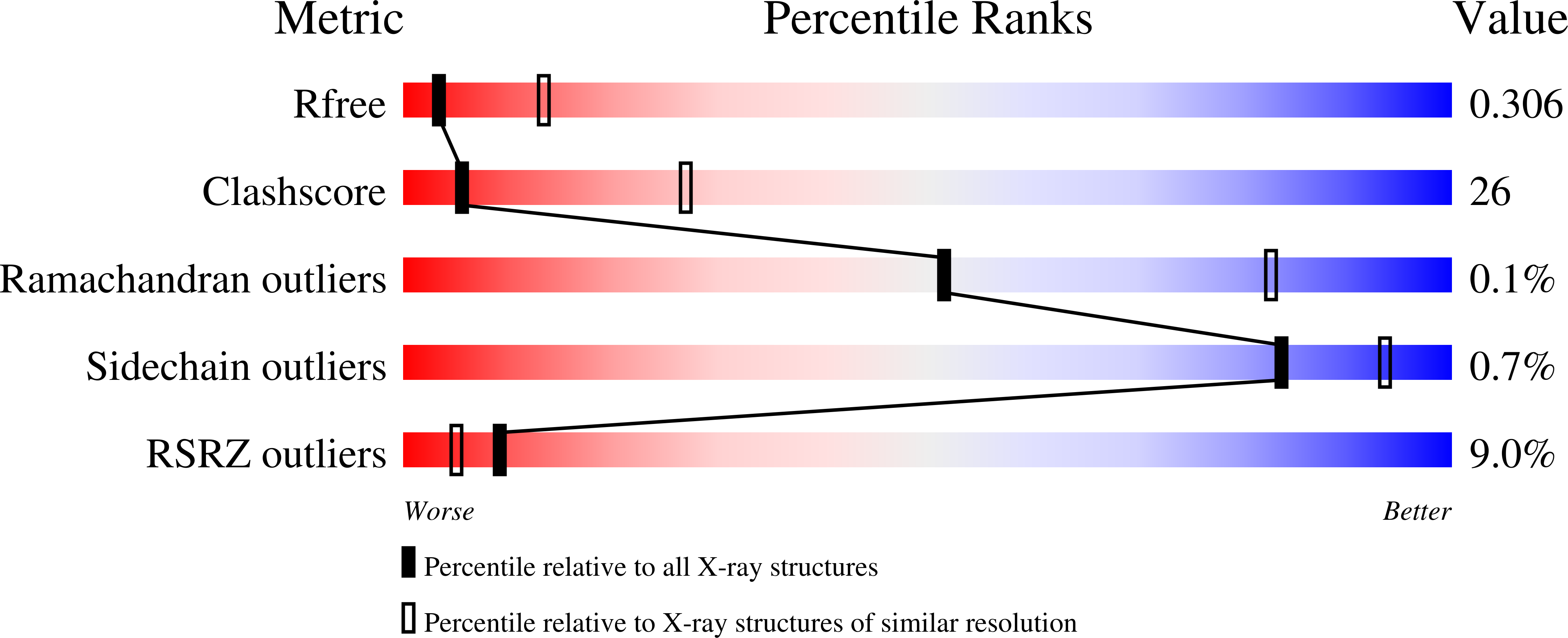
Role of the histone domain in the autoinhibition and activation of the Ras activator Son of Sevenless.
Gureasko, J., Kuchment, O., Makino, D.L., Sondermann, H., Bar-Sagi, D., Kuriyan, J.(2010) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107: 3430-3435
- PubMed: 20133692
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0913915107
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3KSY - PubMed Abstract:
Membrane-bound Ras is activated by translocation of the Son of Sevenless (SOS) protein to the plasma membrane. SOS is inactive unless Ras is bound to an allosteric site on SOS, and the Dbl homology (DH) and Pleckstrin homology (PH) domains of SOS (the DH-PH unit) block allosteric Ras binding. We showed previously that the activity of SOS at the membrane increases with the density of PIP(2) and the local concentration of Ras-GTP, which synergize to release the DH-PH unit. Here we present a new crystal structure of SOS that contains the N-terminal histone domain in addition to the DH-PH unit and the catalytic unit (SOS(HDFC), residues 1-1049). The structure reveals that the histone domain plays a dual role in occluding the allosteric site and in stabilizing the autoinhibitory conformation of the DH-PH unit. Additional insight is provided by kinetic analysis of the activation of membrane-bound Ras by mutant forms of SOS that contain mutations in the histone and the PH domains (E108K, C441Y, and E433K) that are associated with Noonan syndrome, a disease caused by hyperactive Ras signaling. Our results indicate that the histone domain and the DH-PH unit are conformationally coupled, and that the simultaneous engagement of the membrane by a PH domain PIP(2)-binding interaction and electrostatic interactions between a conserved positively charged patch on the histone domain and the negatively charged membrane coincides with a productive reorientation of SOS at the membrane and increased accessibility of both Ras binding sites on SOS.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular and Cell Biology, University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720, USA.