Structure function studies of vaccinia virus host range protein k1 reveal a novel functional surface for ankyrin repeat proteins.
Li, Y., Meng, X., Xiang, Y., Deng, J.(2010) J Virol 84: 3331-3338
- PubMed: 20089642
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.02332-09
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3KEA - PubMed Abstract:
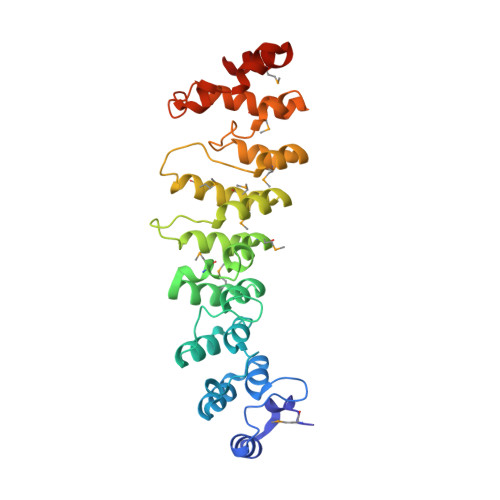
Poxvirus host tropism at the cellular level is regulated by virus-encoded host range proteins acting downstream of virus entry. The functioning mechanisms of most host range proteins are unclear, but many contain multiple ankyrin (ANK) repeats, a motif that is known for ligand interaction through a concave surface. We report here the crystal structure of one of the ANK repeat-containing host range proteins, the vaccinia virus K1 protein. The structure, at a resolution of 2.3 A, showed that K1 consists entirely of ANK repeats, including seven complete ones and two incomplete ones, one each at the N and C terminus. Interestingly, Phe82 and Ser83, which were previously shown to be critical for K1's function, are solvent exposed and located on a convex surface, opposite the consensus ANK interaction surface. The importance of this convex surface was further supported by our additional mutagenesis studies. We found that K1's host range function was negatively affected by substitution of either Asn51 or Cys47 and completely abolished by substitution of both residues. Cys47 and Asn51 are also exposed on the convex surface, spatially adjacent to Phe82 and Ser83. Altogether, our data showed that K1 residues on a continuous convex ANK repeat surface are critical for the host range function, suggesting that K1 functions through ligand interaction and does so with a novel ANK interaction surface.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Microbiology and Immunology, University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, 7703 Floyd Curl Dr., San Antonio, TX 78229, USA.