Crystal Structure of ArgP from Mycobacterium tuberculosis Confirms Two Distinct Conformations of Full-length LysR Transcriptional Regulators and Reveals Its Function in DNA Binding and Transcriptional Regulation.
Zhou, X., Lou, Z., Fu, S., Yang, A., Shen, H., Li, Z., Feng, Y., Bartlam, M., Wang, H., Rao, Z.(2009) J Mol Biol
- PubMed: 20036253
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2009.12.033
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3ISP - PubMed Abstract:
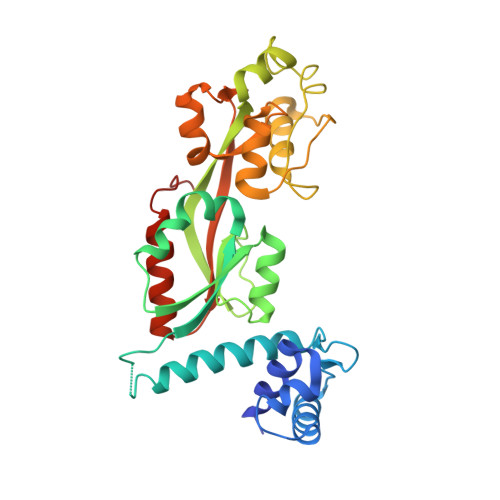
Mycobacterium tuberculosis presents a challenging medical problem partly due to its persistent nonreplicative state. The inhibitor of chromosomal replication (iciA) protein encoded by M. tuberculosis has been suggested to inhibit chromosome replication initiation in vitro. However, iciA has also been identified as arginine permease (ArgP), a regulatory transcription factor for arginine outward transport. In order to understand the function of ArgP, we have determined its crystal structure by X-ray crystallography to a resolution of 2.7 A. ArgP is a member of the LysR-type transcriptional regulators (LTTRs) and forms a homodimer with each subunit containing two domains: a DNA binding domain (DBD) and a regulatory domain (RD). Two conformationally distinct subunits were identified: closed subunit and open subunit. This phenomenon was first observed in LTTR CbnR, but not in LTTR CrgA, and might be common in LTTRs. We identified two forms of dimers: DBD-type dimers and RD-type dimers. The former is confirmed in solution, and the latter is considered to form oligomers during function. We provide the first structural insights into the interaction of the extreme C-terminal residues with the DBD, which is confirmed by mutagenesis and analytical ultracentrifugation to be important for stability of the functional dimer. The structure serves as a model to suggest how three critical aspects, namely, DNA binding, homo-oligomerization, and interaction with RNAP, are mediated during regulation processing. A model is proposed for the LysR family of dimeric regulators.
Organizational Affiliation:
National Laboratory of Macromolecules, Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Science, Beijing 100101, China.