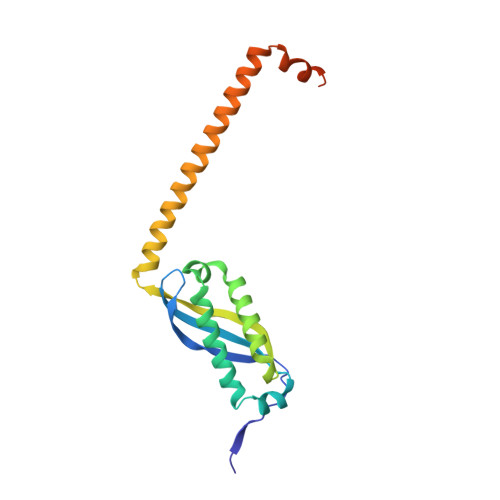
Crystal structure of a core domain of stomatin from Pyrococcus horikoshii Illustrates a novel trimeric and coiled-coil fold
Yokoyama, H., Fujii, S., Matsui, I.(2008) J Mol Biol 376: 868-878
- PubMed: 18182167
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2007.12.024
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3BK6 - PubMed Abstract:
Stomatin is a major integral membrane protein of human erythrocytes, the absence of which is associated with a form of hemolytic anemia known as hereditary stomatocytosis. However, the function of stomatin is not fully understood. An open reading frame, PH1511, from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus horikoshii encodes p-stomatin, a prokaryotic stomatin. Here, we report the first crystal structure of a stomatin ortholog, the core domain of the p-stomatin PH1511p (residues 56-234 of PH1511p, designated as PhSto(CD)). PhSto(CD) forms a novel homotrimeric structure. Three alpha/beta domains form a triangle of about 50 A on each side, and three alpha-helical segments of about 60 A in length extend from the apexes of the triangle. The alpha/beta domain of PhSto(CD) is partly similar in structure to the band-7 domain of mouse flotillin-2. While the alpha/beta domain is relatively rigid, the alpha-helical segment shows conformational flexibility, adapting to the neighboring environment. One alpha-helical segment forms an anti-parallel coiled coil with another alpha-helical segment from a symmetry-related molecule. The alpha-helical segment shows a heptad repeat pattern, and mainly hydrophobic residues form a coiled-coil interface. According to chemical cross-linking experiments, PhSto(CD) would be able to assemble into an oligomeric form. The coiled-coil fold observed in the crystal probably contributes to self-association.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Shizuoka, Shizuoka 422-8526, Japan.