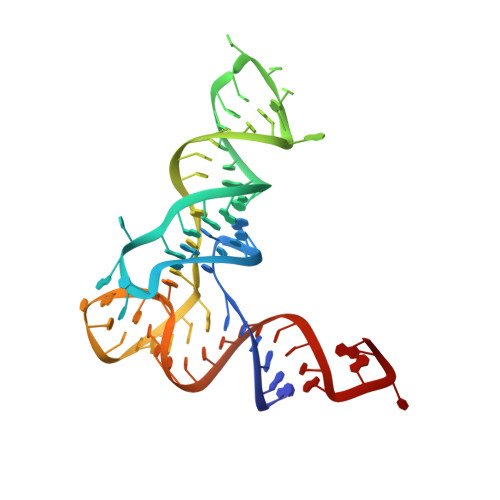
Two enzymes bound to one transfer RNA assume alternative conformations for consecutive reactions.
Ito, T., Yokoyama, S.(2010) Nature 467: 612-616
- PubMed: 20882017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09411
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3AKZ, 3AL0 - PubMed Abstract:
In most bacteria and all archaea, glutamyl-tRNA synthetase (GluRS) glutamylates both tRNA(Glu) and tRNA(Gln), and then Glu-tRNA(Gln) is selectively converted to Gln-tRNA(Gln) by a tRNA-dependent amidotransferase. The mechanisms by which the two enzymes recognize their substrate tRNA(s), and how they cooperate with each other in Gln-tRNA(Gln) synthesis, remain to be determined. Here we report the formation of the 'glutamine transamidosome' from the bacterium Thermotoga maritima, consisting of tRNA(Gln), GluRS and the heterotrimeric amidotransferase GatCAB, and its crystal structure at 3.35 A resolution. The anticodon-binding body of GluRS recognizes the common features of tRNA(Gln) and tRNA(Glu), whereas the tail body of GatCAB recognizes the outer corner of the L-shaped tRNA(Gln) in a tRNA(Gln)-specific manner. GluRS is in the productive form, as its catalytic body binds to the amino-acid-acceptor arm of tRNA(Gln). In contrast, GatCAB is in the non-productive form: the catalytic body of GatCAB contacts that of GluRS and is located near the acceptor stem of tRNA(Gln), in an appropriate site to wait for the completion of Glu-tRNA(Gln) formation by GluRS. We identified the hinges between the catalytic and anticodon-binding bodies of GluRS and between the catalytic and tail bodies of GatCAB, which allow both GluRS and GatCAB to adopt the productive and non-productive forms. The catalytic bodies of the two enzymes compete for the acceptor arm of tRNA(Gln) and therefore cannot assume their productive forms simultaneously. The transition from the present glutamylation state, with the productive GluRS and the non-productive GatCAB, to the putative amidation state, with the non-productive GluRS and the productive GatCAB, requires an intermediate state with the two enzymes in their non-productive forms, for steric reasons. The proposed mechanism explains how the transamidosome efficiently performs the two consecutive steps of Gln-tRNA(Gln) formation, with a low risk of releasing the unstable intermediate Glu-tRNA(Gln).
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biophysics and Biochemistry, Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033, Japan.