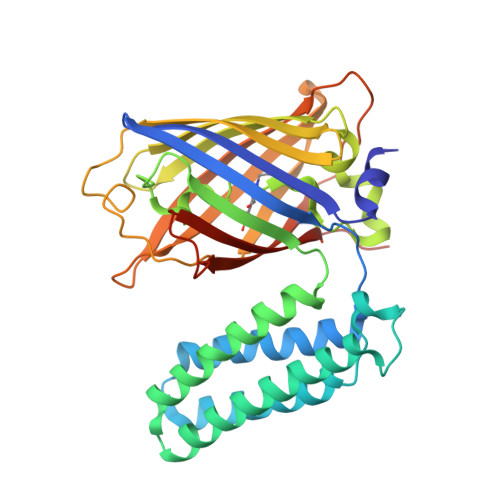
Structural basis for efficient chromophore communication and energy transfer in a constructed didomain protein scaffold.
Arpino, J.A., Czapinska, H., Piasecka, A., Edwards, W.R., Barker, P., Gajda, M.J., Bochtler, M., Jones, D.D.(2012) J Am Chem Soc 134: 13632-13640
- PubMed: 22822710
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ja301987h
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3U8P - PubMed Abstract:
The construction of useful functional biomolecular components not currently part of the natural repertoire is central to synthetic biology. A new light-capturing ultra-high-efficiency energy transfer protein scaffold has been constructed by coupling the chromophore centers of two normally unrelated proteins: the autofluorescent protein enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) and the heme-binding electron transfer protein cytochrome b(562) (cyt b(562)). Using a combinatorial domain insertion strategy, a variant was isolated in which resonance energy transfer from the donor EGFP to the acceptor cyt b(562) was close to 100% as evident by virtually full fluorescence quenching on heme binding. The fluorescence signal of the variant was also sensitive to the reactive oxygen species H(2)O(2), with high signal gain observed due to the release of heme. The structure of oxidized holoprotein, determined to 2.75 Å resolution, revealed that the two domains were arranged side-by-side in a V-shape conformation, generating an interchromophore distance of ~17 Å (14 Å edge-to-edge). Critical to domain arrangement is the formation of a molecular pivot point between the two domains as a result of different linker sequence lengths at each domain junction and formation of a predominantly polar interdomain interaction surface. The retrospective structural analysis has provided an explanation for the basis of the observed highly efficient energy transfer through chromophore arrangement in the directly evolved protein scaffold and provides an insight into the molecular principles by which to design new proteins with coupled functions.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Biosciences, Main Building, Park Place, Cardiff University, Cardiff CF10 3AT, United Kingdom.