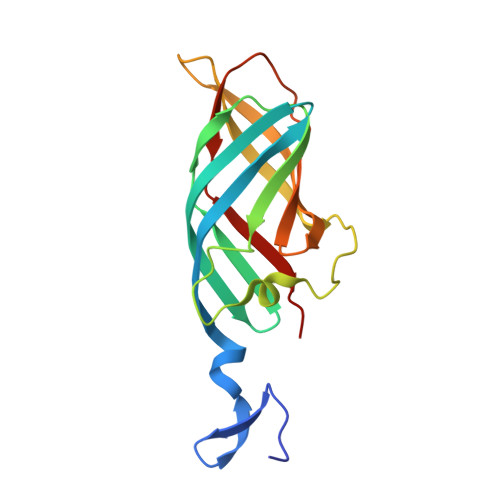
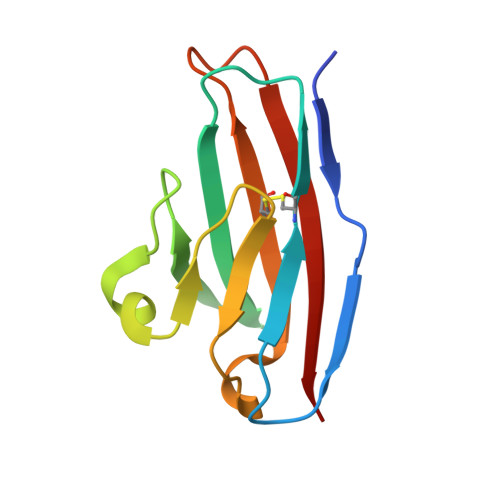
Structure of reovirus sigma1 in complex with its receptor junctional adhesion molecule-A
Kirchner, E., Guglielmi, K.M., Strauss, H.M., Dermody, T.S., Stehle, T.(2008) PLoS Pathog 4: e1000235-e1000235
- PubMed: 19079583
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1000235
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3EOY - PubMed Abstract:
Viral attachment to specific host receptors is the first step in viral infection and serves an essential function in the selection of target cells. Mammalian reoviruses are highly useful experimental models for studies of viral pathogenesis and show promise as vectors for oncolytics and vaccines. Reoviruses engage cells by binding to carbohydrates and the immunoglobulin superfamily member, junctional adhesion molecule-A (JAM-A). JAM-A exists at the cell surface as a homodimer formed by extensive contacts between its N-terminal immunoglobulin-like domains. We report the crystal structure of reovirus attachment protein sigma1 in complex with a soluble form of JAM-A. The sigma1 protein disrupts the JAM-A dimer, engaging a single JAM-A molecule via virtually the same interface that is used for JAM-A homodimerization. Thus, reovirus takes advantage of the adhesive nature of an immunoglobulin-superfamily receptor by usurping the ligand-binding site of this molecule to attach to the cell surface. The dissociation constant (K(D)) of the interaction between sigma1 and JAM-A is 1,000-fold lower than that of the homophilic interaction between JAM-A molecules, indicating that JAM-A strongly prefers sigma1 as a ligand. Analysis of reovirus mutants engineered by plasmid-based reverse genetics revealed residues in sigma1 required for binding to JAM-A and infectivity of cultured cells. These studies define biophysical mechanisms of reovirus cell attachment and provide a platform for manipulating reovirus tropism to enhance vector targeting.
Organizational Affiliation:
Interfaculty Institute for Biochemistry, University of Tuebingen, Tuebingen, Germany.