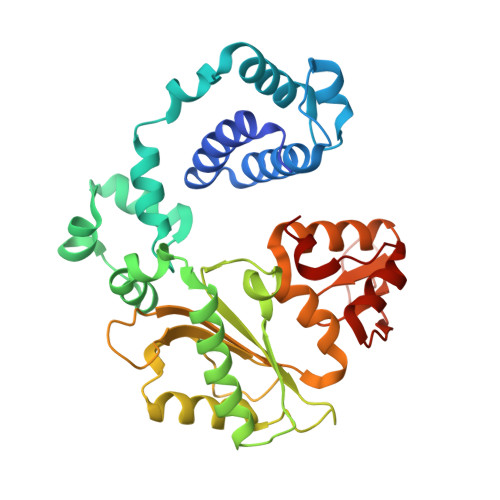
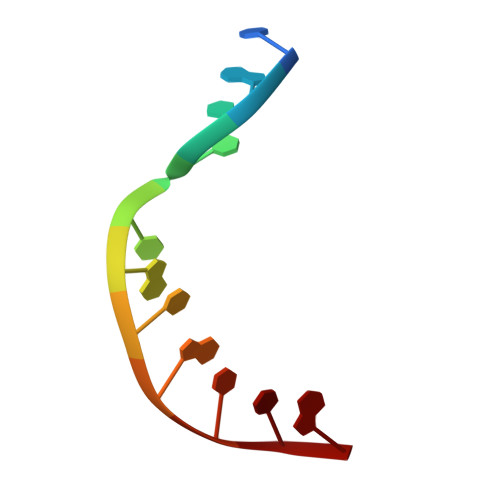
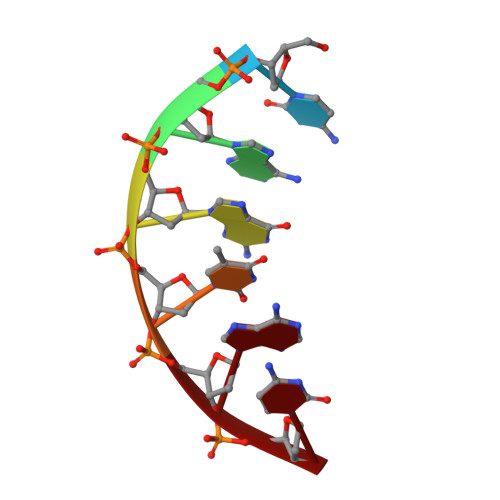
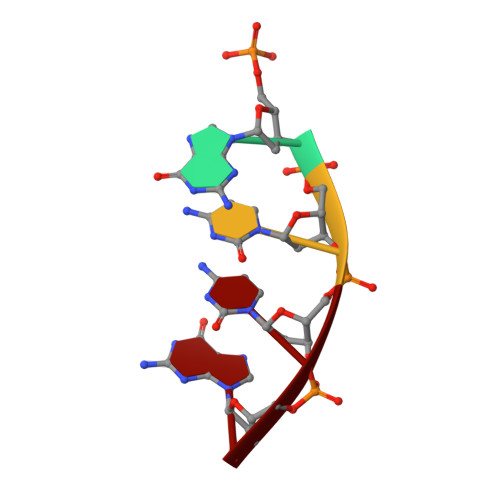
Substrate-induced DNA strand misalignment during catalytic cycling by DNA polymerase lambda.
Bebenek, K., Garcia-Diaz, M., Foley, M.C., Pedersen, L.C., Schlick, T., Kunkel, T.A.(2008) EMBO Rep 9: 459-464
- PubMed: 18369368
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/embor.2008.33
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3C5F, 3C5G - PubMed Abstract:
The simple deletion of nucleotides is common in many organisms. It can be advantageous when it activates genes beneficial to microbial survival in adverse environments, and deleterious when it mutates genes relevant to survival, cancer or degenerative diseases. The classical idea is that simple deletions arise by strand slippage. A prime opportunity for slippage occurs during DNA synthesis, but it remains unclear how slippage is controlled during a polymerization cycle. Here, we report crystal structures and molecular dynamics simulations of mutant derivatives of DNA polymerase lambda bound to a primer-template during strand slippage. Relative to the primer strand, the template strand is in multiple conformations, indicating intermediates on the pathway to deletion mutagenesis. Consistent with these intermediates, the mutant polymerases generate single-base deletions at high rates. The results indicate that dNTP-induced template strand repositioning during conformational rearrangements in the catalytic cycle is crucial to controlling the rate of strand slippage.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Structural Biology and Laboratory of Molecular Genetics, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, NIH, Research Triangle Park, North Carolina 27709, USA.