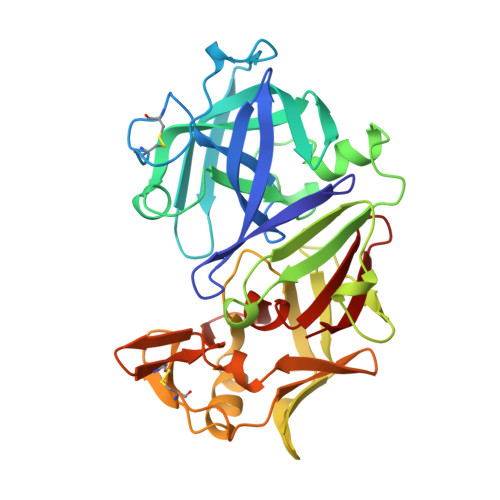
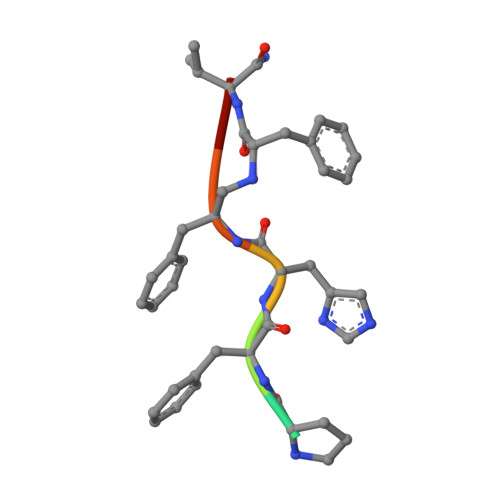
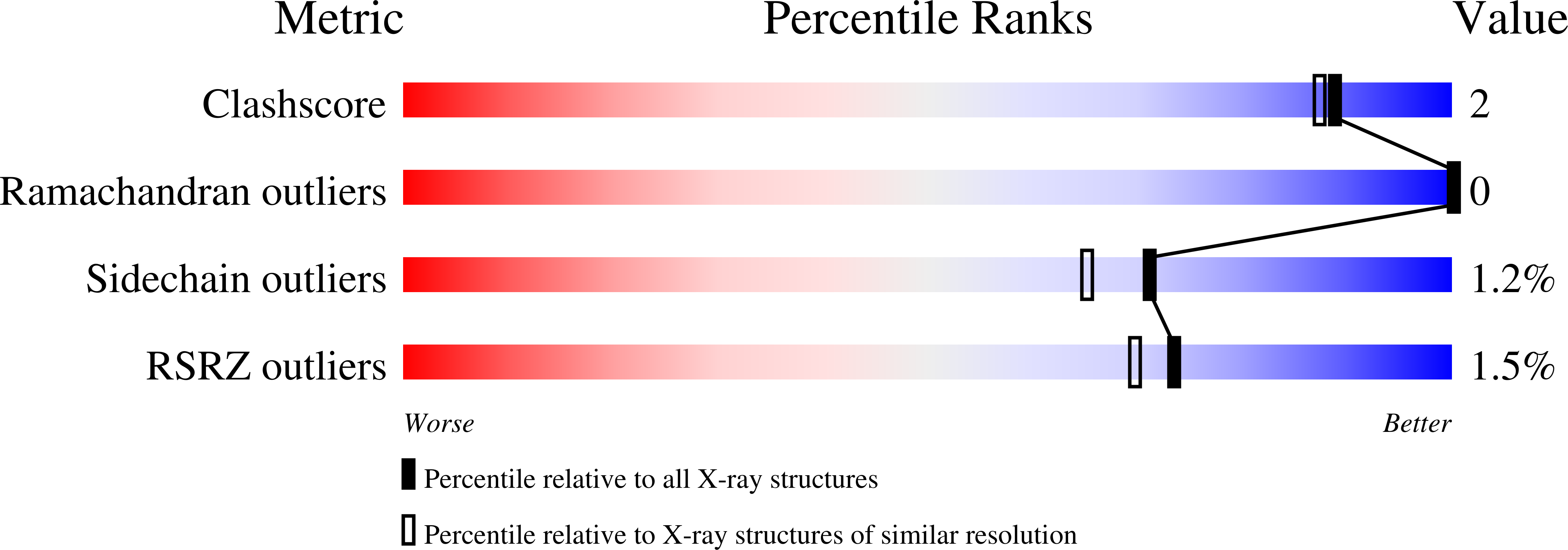Binding of a reduced peptide inhibitor to the aspartic proteinase from Rhizopus chinensis: implications for a mechanism of action.
Suguna, K., Padlan, E.A., Smith, C.W., Carlson, W.D., Davies, D.R.(1987) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 84: 7009-7013
- PubMed: 3313384
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.84.20.7009
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3APR - PubMed Abstract:
A peptide inhibitor, having the sequence D-His-Pro-Phe-His-Phe psi [CH2-NH]Phe-Val-Tyr, with a reduced bond between the two adjacent phenylalanines, has been diffused into crystals of the aspartic proteinase from Rhizopus chinensis (rhizopuspepsin, EC 3.4.23.6). X-ray diffraction data to 1.8-A resolution have been collected on the complex, which has been subjected to restrained least-squares refinement to an R-factor (R equals the sum of the absolute value of the difference between the observed and calculated structure factor amplitudes divided by the sum of the observed structure factor amplitudes) of 14.7%. The inhibitor lies within the major groove of the enzyme and is clearly defined with the exception of the amino-terminal D-histidine and the carboxyl-terminal tyrosine. The reduced peptide bond is located in the active site with close contacts to the two catalytic aspartyl groups. The active-site water molecule that is held between the two carboxyl groups is displaced by the inhibitor, as are a number of other water molecules seen in the binding groove of the native enzyme. A mechanism of action for this class of enzymes is proposed from these results.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Molecular Biology, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Bethesda, MD 20892.