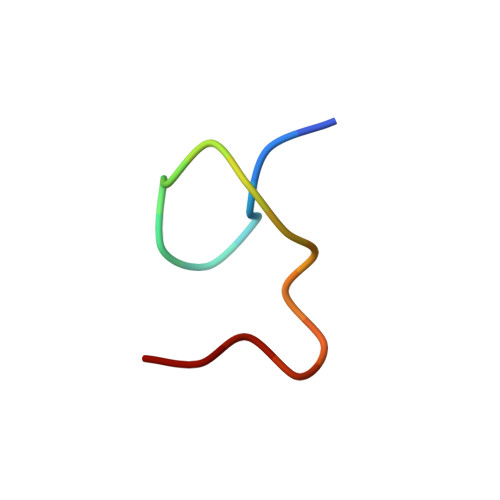
High-resolution structure of an HIV zinc fingerlike domain via a new NMR-based distance geometry approach.
Summers, M.F., South, T.L., Kim, B., Hare, D.R.(1990) Biochemistry 29: 329-340
- PubMed: 2105740
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00454a005
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2ZNF - PubMed Abstract:
A new method is described for determining molecular structures from NMR data. The approach utilizes 2D NOESY back-calculations to generate simulated spectra for structures obtained from distance geometry (DG) computations. Comparison of experimental and back-calculated spectra, including analysis of cross-peak buildup and auto-peak decay with increasing mixing time, provides a quantitative measure of the consistence between the experimental data and generated structures and allows for use of tighter interproton distance constraints. For the first time, the "goodness" of the generated structures is evaluated on the basis of their consistence with the actual experimental data rather than on the basis of consistence with other generated structures. This method is applied to the structure determination of an 18-residue peptide with an amino acid sequence comprising the first zinc fingerlike domain from the gag protein p55 of HIV. This is the first structure determination to atomic resolution for a retroviral zinc fingerlike complex. The peptide [Zn(p55F1)] exhibits a novel folding pattern that includes type I and type II NH-S tight turns and is stabilized both by coordination of the three Cys and one His residues to zinc and by extensive internal hydrogen bonding. The backbone folding is significantly different from that of a "classical" DNA-binding zinc finger. Residues C(1)-F(2)-N(3)-C(4)-G(5)-K(6) fold in a manner virtually identical with the folding observed by X-ray crystallography for related residues in the iron domain of rubredoxin; superposition of all main-chain and Cys side-chain atoms of residues C(1)-K(6) of Zn(p55F1) onto residues C(6)-Y(11) and C(39)-V(44) of rubredoxin gives RMSDs of 0.46 and 0.35 A, respectively. The side chains of conservatively substituted Phe and Ile residues implicated in genomic RNA recognition form a hydrophobic patch on the peptide surface.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Maryland Baltimore County 21228.