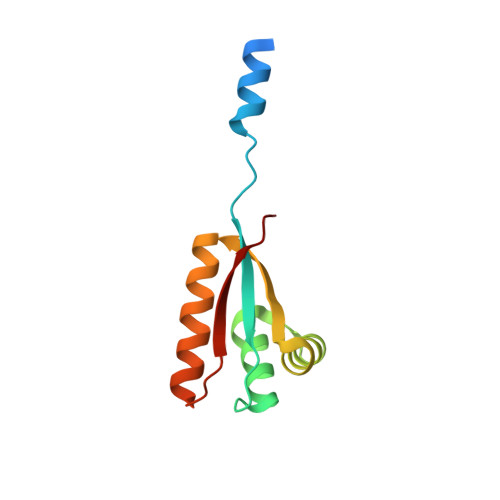
Structural Basis of N-End Rule Substrate Recognition in Escherichia Coli by the Clpap Adaptor Protein Clps.
Schuenemann, V.J., Kralik, S.M., Albrecht, R., Spall, S.K., Truscott, K.N., Dougan, D.A., Zeth, K.(2009) EMBO Rep 10: 508
- PubMed: 19373253
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/embor.2009.62
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2W9R, 2WA8, 2WA9 - PubMed Abstract:
In Escherichia coli, the ClpAP protease, together with the adaptor protein ClpS, is responsible for the degradation of proteins bearing an amino-terminal destabilizing amino acid (N-degron). Here, we determined the three-dimensional structures of ClpS in complex with three peptides, each having a different destabilizing residue--Leu, Phe or Trp--at its N terminus. All peptides, regardless of the identity of their N-terminal residue, are bound in a surface pocket on ClpS in a stereo-specific manner. Several highly conserved residues in this binding pocket interact directly with the backbone of the N-degron peptide and hence are crucial for the binding of all N-degrons. By contrast, two hydrophobic residues define the volume of the binding pocket and influence the specificity of ClpS. Taken together, our data suggest that ClpS has been optimized for the binding and delivery of N-degrons containing an N-terminal Phe or Leu.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Protein Evolution, Max Planck Institute for Developmental Biology, Spemannstrasse 35, Tübingen D-72076, Germany.