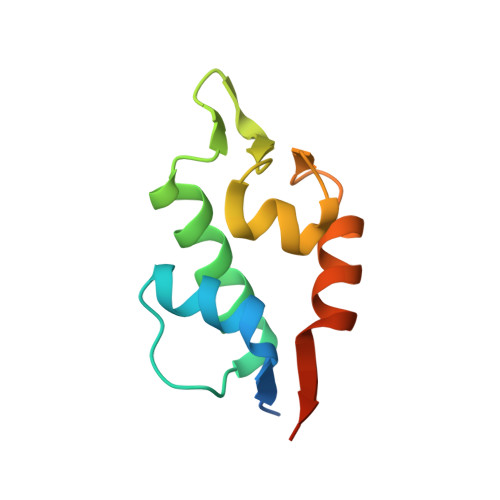
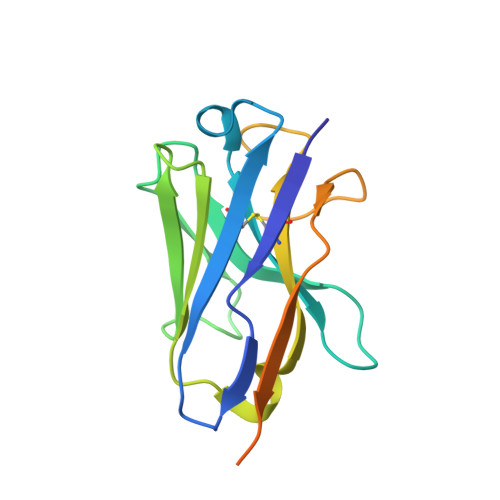
Structure of Human Mdm4 N-Terminal Domain Bound to a Single-Domain Antibody.
Yu, G.W., Vaysburd, M., Allen, M.D., Settanni, G., Fersht, A.R.(2009) J Mol Biol 385: 1578
- PubMed: 19084022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2008.11.043
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2VYR - PubMed Abstract:
The N-terminal domain of MDM4 binds to the N-terminal transactivation domain of the tumor suppressor p53 and is an important negative regulator of its transactivation activity. As such, inhibition of the binding of MDM4 to p53 is a target for anticancer therapy. The protein has not been crystallized satisfactorily for structural studies without the addition of an N-terminal p53 peptide. We selected a single-domain antibody (VH9) that bound to the human domain with a dissociation constant of 44 nM. We solved the structure of the complex at 2.0-A resolution. The asymmetric unit contained eight molecules of VH9 and four molecules of MDM4. A molecule of VH9 was located in each transactivation domain binding site, and the four non-MDM4-bound VH9 domains provided additional crystal contacts. There are differences between the structures of human MDM4 domain bound to VH9 and those of human and zebra fish MDM4 bound to a p53 peptide. Molecular dynamics simulations showed that the binding pocket in the three MDM4 structures converged to a common conformation after removal of the ligands, indicating that the differences are due to induced fit. The largest conformational changes were for the MDM4 molecules bound to p53. The simulated and observed structures should aid rational drug design. The use of single-domain antibodies to aid crystallization by creating a molecular scaffold may have a wider range of applications.
Organizational Affiliation:
Centre for Protein Engineering, Medical Research Council, Cambridge, UK.