Increased Stability and DNA Site Discrimination of "Single Chain" Variants of the Dimeric beta-Barrel DNA Binding Domain of the Human Papillomavirus E2 Transcriptional Regulator.
Dellarole, M., Sanchez, I.E., Freire, E., Prat-Gay, G.(2007) Biochemistry 46: 12441-12450
- PubMed: 17915949
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi701104q
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
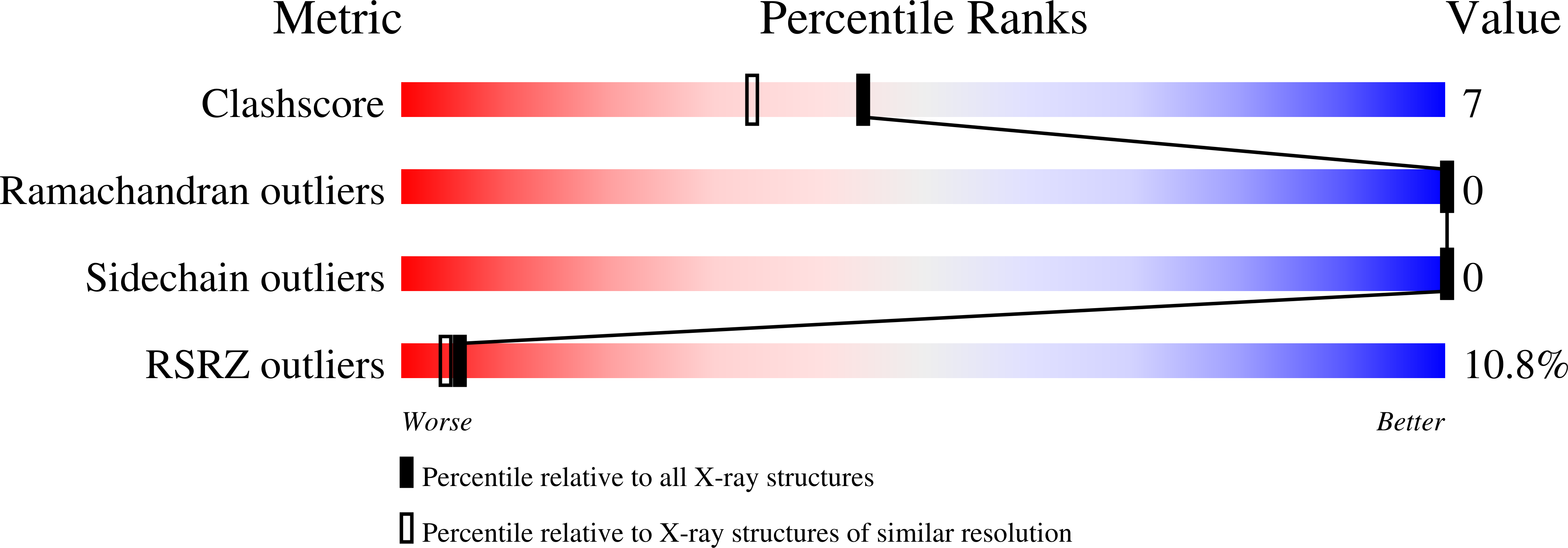
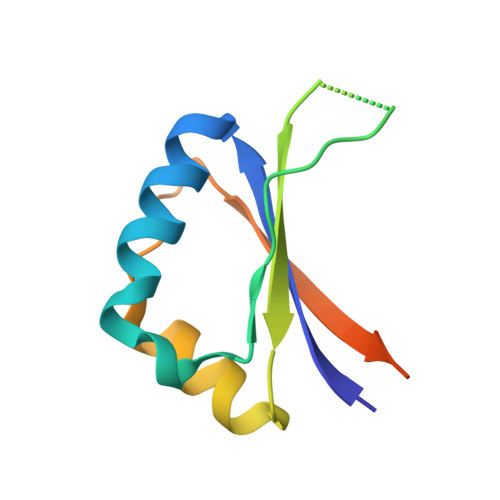
2Q79 - PubMed Abstract:
Human papillomavirus infects millions of people worldwide and is a causal agent of cervical cancer in women. The HPV E2 protein controls the expression of all viral genes through binding of its dimeric C-terminal domain (E2C) to its target DNA site. We engineered monomeric versions of the HPV16 E2C, in order to probe the link of the dimeric beta-barrel fold to stability, dimerization, and DNA binding. Two single-chain variants, with 6 and 12 residue linkers (scE2C-6 and scE2C-12), were purified and characterized. Spectroscopy and crystallography show that the native structure is unperturbed in scE2C-12. The single chain variants are stabilized with respect to E2C, with effective concentrations of 0.6 to 6 mM. The early folding events of the E2C dimer and scE2C-12 are very similar and include formation of a compact species in the submillisecond time scale and a non-native monomeric intermediate with a half-life of 25 ms. However, monomerization changes the unfolding mechanism of the linked species from two-state to three-state, with a high-energy intermediate. Binding to the specific target site is up to 5-fold tighter in the single chain variants. Nonspecific DNA binding is up to 7-fold weaker in the single chain variants, leading to an overall 10-fold increased site discrimination capacity, the largest described so far for linked DNA binding domains. Titration calorimetric binding analysis, however, shows almost identical behavior for dimer and single-chain species, suggesting very subtle changes behind the increased specificity. Global analysis of the mechanisms probed suggests that the dynamics of the E2C domain, rather than the structure, are responsible for the differential properties. Thus, the plastic and dimeric nature of the domain did not evolve for a maximum affinity, specificity, and stability of the quaternary structure, likely because of regulatory reasons and for roles other than DNA binding played by partly folded dimeric or monomeric conformers.
Organizational Affiliation:
Instituto Leloir and IIBBA-Conicet, Patricias Argentinas 435 (1405), Buenos Aires, Argentina.