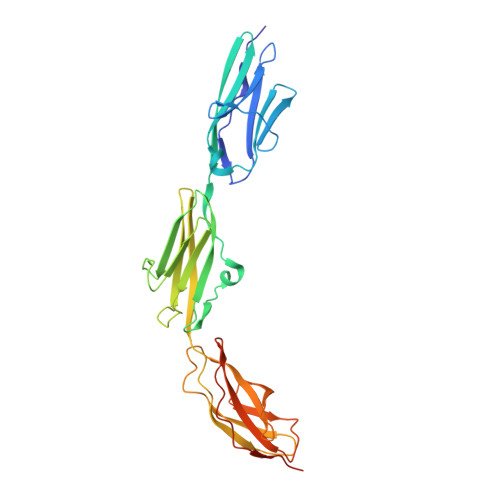
Molecular determinants for the recruitment of the ubiquitin-ligase MuRF-1 onto M-line titin.
Mrosek, M., Labeit, D., Witt, S., Heerklotz, H., von Castelmur, E., Labeit, S., Mayans, O.(2007) FASEB J 21: 1383-1392
- PubMed: 17215480
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.06-7644com
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2NZI - PubMed Abstract:
Titin forms an intrasarcomeric filament system in vertebrate striated muscle, which has elastic and signaling properties and is thereby central to mechanotransduction. Near its C-terminus and directly preceding a kinase domain, titin contains a conserved pattern of Ig and FnIII modules (Ig(A168)-Ig(A169)-FnIII(A170), hereby A168-A170) that recruits the E3 ubiquitin-ligase MuRF-1 to the filament. This interaction is thought to regulate myofibril turnover and the trophic state of muscle. We have elucidated the crystal structure of A168-A170, characterized MuRF-1 variants by circular dichroism (CD) and SEC-MALS, and studied the interaction of both components by isothermal calorimetry, SPOTS blots, and pull-down assays. This has led to the identification of the molecular determinants of the binding. A168-A170 shows an extended, rigid architecture, which is characterized by a shallow surface groove that spans its full length and a distinct loop protrusion in its middle point. In MuRF-1, a C-terminal helical domain is sufficient to bind A168-A170 with high affinity. This helical region predictably docks into the surface groove of A168-A170. Furthermore, pull-down assays demonstrate that the loop protrusion in A168-A170 is a key mediator of MuRF-1 recognition. Our findings indicate that this region of titin could serve as a target to attempt therapeutic inhibition of MuRF-1-mediated muscle turnover, where binding of small molecules to its distinctive structural features could block MuRF-1 access.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Structural Biology, Biozentrum, University of Basel, Klingelbergstr. 70, CH-4056 Basel, Switzerland.