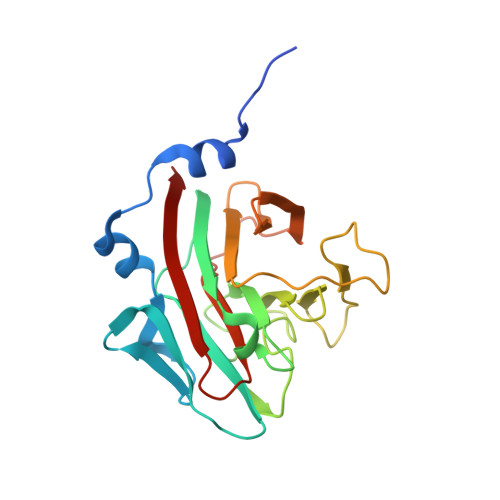
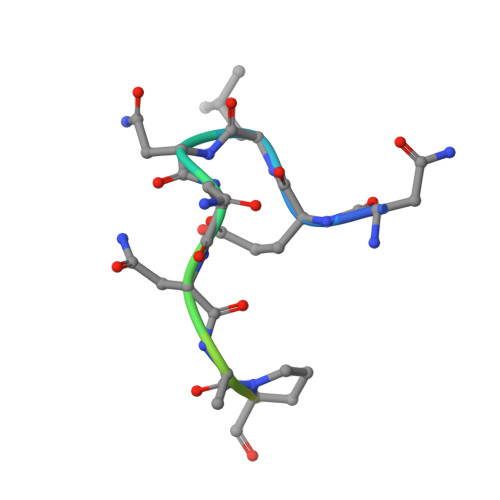
Structural Basis for Par-4 Recognition by the Spry Domain-and Socs Box-Containing Proteins Spsb1, Spsb2, and Spsb4.
Filippakopoulos, P., Low, A., Sharpe, T.D., Uppenberg, J., Yao, S., Kuang, Z., Savitsky, P., Lewis, R.S., Nicholson, S.E., Norton, R.S., Bullock, A.(2010) J Mol Biol 401: 389
- PubMed: 20561531
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2010.06.017
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2JK9, 2V24, 3EMW, 3F2O - PubMed Abstract:
The mammalian SPRY domain- and SOCS box-containing proteins, SPSB1 to SPSB4, belong to the SOCS box family of E3 ubiquitin ligases. Substrate recognition sites for the SPRY domain are identified only for human Par-4 (ELNNNL) and for the Drosophila orthologue GUSTAVUS binding to the DEAD-box RNA helicase VASA (DINNNN). To further investigate this consensus motif, we determined the crystal structures of SPSB1, SPSB2, and SPSB4, as well as their binding modes and affinities for both Par-4 and VASA. Mutation of each of the three Asn residues in Par-4 abrogated binding to all three SPSB proteins, while changing EL to DI enhanced binding. By comparison to SPSB1 and SPSB4, the more divergent protein SPSB2 showed only weak binding to Par-4 and was hypersensitive to DI substitution. Par-4((59-77)) binding perturbed NMR resonances from a number of SPSB2 residues flanking the ELNNN binding site, including loop D, which binds the EL/DI sequence. Although interactions with the consensus peptide motif were conserved in all structures, flanking sites in SPSB2 were identified as sites of structural change. These structural changes limit high-affinity interactions for SPSB2 to aspartate-containing sequences, whereas SPSB1 and SPSB4 bind strongly to both Par-4 and VASA peptides.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Genomics Consortium, University of Oxford, Old Road Campus, Roosevelt Drive, Oxford OX3 7DQ, UK.