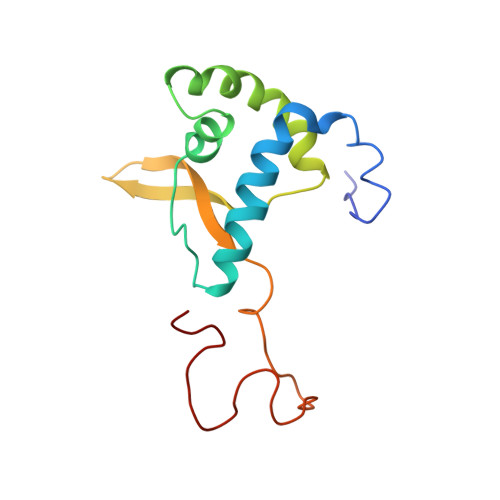
The carboxyl-terminal nucleoplasmic region of MAN1 exhibits a DNA binding winged helix domain.
Caputo, S., Couprie, J., Duband-Goulet, I., Konde, E., Lin, F., Braud, S., Gondry, M., Gilquin, B., Worman, H.J., Zinn-Justin, S.(2006) J Biol Chem 281: 18208-18215
- PubMed: 16648637
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M601980200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2CH0 - PubMed Abstract:
MAN1 is an integral protein of the inner nuclear membrane that interacts with nuclear lamins and emerin, thus playing a role in nuclear organization. It also binds to chromatin-associated proteins and transcriptional regulators, including the R-Smads, Smad1, Smad2, and Smad3. Mutations in the human gene encoding MAN1 cause sclerosing bone dysplasias, which sometimes have associated skin abnormalities. At the molecular level, these mutations lead to loss of the MAN1-R-Smads interaction, thus perturbing transforming growth factor beta superfamily signaling pathway. As a first step to understanding the physical basis of MAN1 interaction with R-Smads, we here report the structural characterization of the carboxyl-terminal nucleoplasmic region of MAN1, which is responsible for Smad binding. This region exhibits an amino-terminal globular domain adopting a winged helix fold, as found in several Smad-associated sequence-specific DNA binding factors. Consistently, it binds to DNA through the positively charged recognition helix H3 of its winged helix motif. However, it does not show the predicted carboxyl-terminal U2AF homology domain in solution, suggesting that the folding and stability of such a domain in MAN1 depend upon binding to an unidentified partner. Modeling the complex between DNA and the winged helix domain shows that the regions involved in DNA binding are essentially distinct from those reported to be involved in Smad binding. This suggests that MAN1 binds simultaneously to R-Smads and their targeted DNA sequences.
Organizational Affiliation:
Département d'Ingénierie et d'Etudes des Protéines/Direction des Sciences du Vivant, Bâtiment 152, Commissariat à l'Energie Atomique Saclay, 91191 Gif-sur-Yvette Cedex, France.