Metal Ion-Dependent Heavy Chain Transfer Activity of Tsg-6 Mediates Assembly of the Cumulus-Oocyte Matrix.
Briggs, D.C., Birchenough, H.L., Ali, T., Rugg, M.S., Waltho, J.P., Ievoli, E., Jowitt, T.A., Enghild, J.J., Richter, R.P., Salustri, A., Milner, C.M., Day, A.J.(2015) J Biol Chem 290: 28708
- PubMed: 26468290
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.669838
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
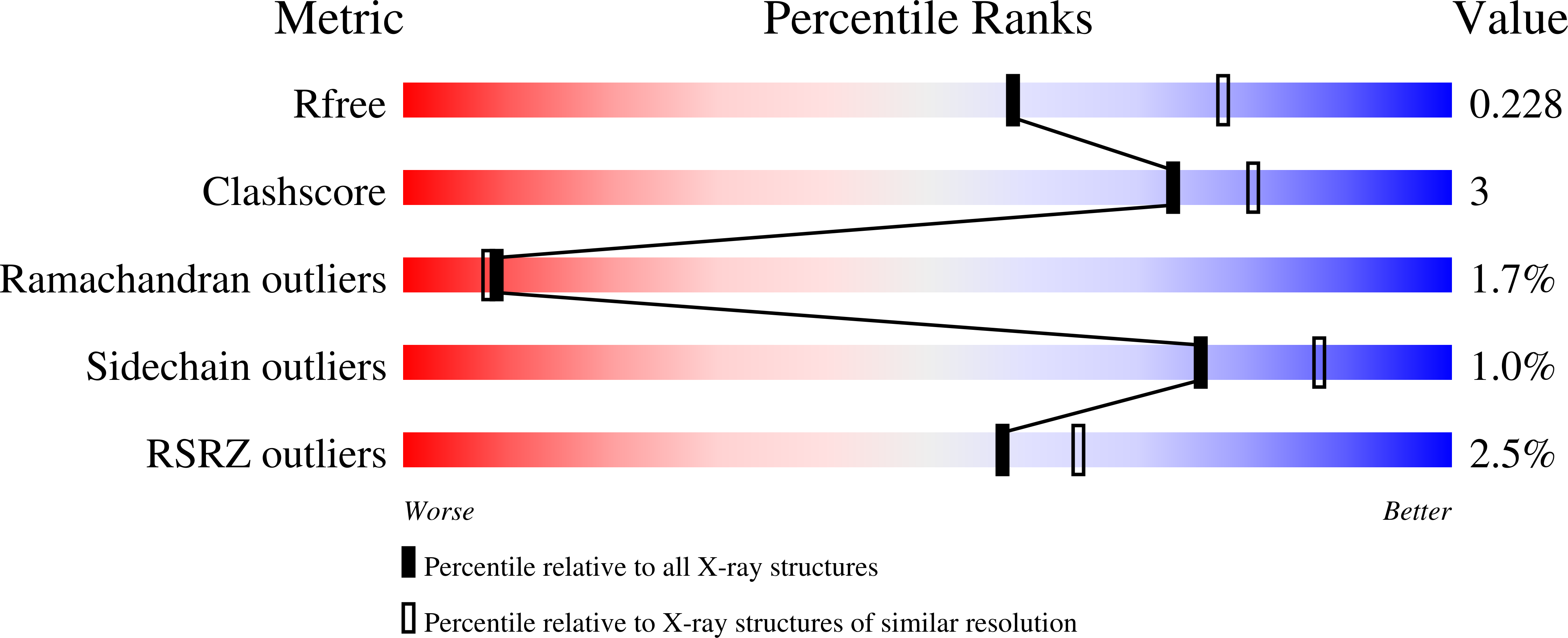
2WNO - PubMed Abstract:
The matrix polysaccharide hyaluronan (HA) has a critical role in the expansion of the cumulus cell-oocyte complex (COC), a process that is necessary for ovulation and fertilization in most mammals. Hyaluronan is organized into a cross-linked network by the cooperative action of three proteins, inter-α-inhibitor (IαI), pentraxin-3, and TNF-stimulated gene-6 (TSG-6), driving the expansion of the COC and providing the cumulus matrix with its required viscoelastic properties. Although it is known that matrix stabilization involves the TSG-6-mediated transfer of IαI heavy chains (HCs) onto hyaluronan (to form covalent HC·HA complexes that are cross-linked by pentraxin-3) and that this occurs via the formation of covalent HC·TSG-6 intermediates, the underlying molecular mechanisms are not well understood. Here, we have determined the tertiary structure of the CUB module from human TSG-6, identifying a calcium ion-binding site and chelating glutamic acid residue that mediate the formation of HC·TSG-6. This occurs via an initial metal ion-dependent, non-covalent, interaction between TSG-6 and HCs that also requires the presence of an HC-associated magnesium ion. In addition, we have found that the well characterized hyaluronan-binding site in the TSG-6 Link module is not used for recognition during transfer of HCs onto HA. Analysis of TSG-6 mutants (with impaired transferase and/or hyaluronan-binding functions) revealed that although the TSG-6-mediated formation of HC·HA complexes is essential for the expansion of mouse COCs in vitro, the hyaluronan-binding function of TSG-6 does not play a major role in the stabilization of the murine cumulus matrix.
Organizational Affiliation:
From the Wellcome Trust Centre for Cell-Matrix Research and the Faculty of Life Sciences, University of Manchester, Oxford Road, Manchester M13 9PT, United Kingdom.