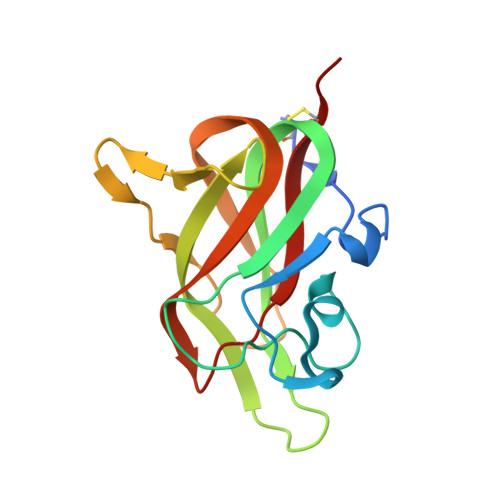
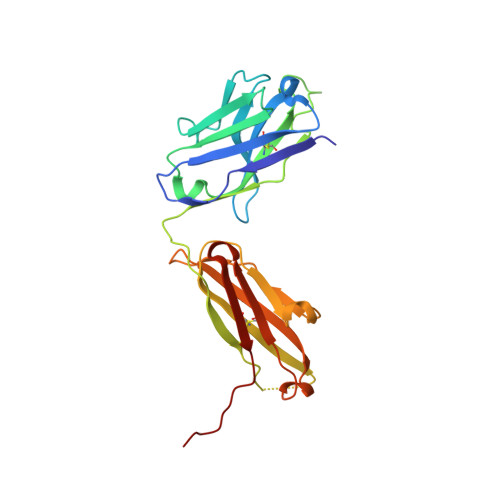
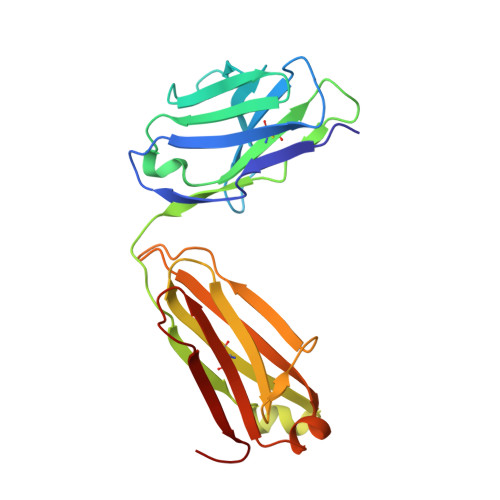
Structural studies of neuropilin/antibody complexes provide insights into semaphorin and VEGF binding
Appleton, B.A., Wu, P., Maloney, J., Yin, J., Liang, W.C., Stawicki, S., Mortara, K., Bowman, K.K., Elliott, J.M., Desmarais, W., Bazan, J.F., Bagri, A., Tessier-Lavigne, M., Koch, A.W., Wu, Y., Watts, R.J., Wiesmann, C.(2007) EMBO J 26: 4902-4912
- PubMed: 17989695
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601906
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2QQI, 2QQJ, 2QQL, 2QQN, 2QQO - PubMed Abstract:
Neuropilins (Nrps) are co-receptors for class 3 semaphorins and vascular endothelial growth factors and important for the development of the nervous system and the vasculature. The extracellular portion of Nrp is composed of two domains that are essential for semaphorin binding (a1a2), two domains necessary for VEGF binding (b1b2), and one domain critical for receptor dimerization (c). We report several crystal structures of Nrp1 and Nrp2 fragments alone and in complex with antibodies that selectively block either semaphorin or vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) binding. In these structures, Nrps adopt an unexpected domain arrangement in which the a2, b1, and b2 domains form a tightly packed core that is only loosely connected to the a1 domain. The locations of the antibody epitopes together with in vitro experiments indicate that VEGF and semaphorin do not directly compete for Nrp binding. Based upon our structural and functional data, we propose possible models for ligand binding to neuropilins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Protein Engineering, Genentech, Inc., South San Francisco, CA 94080, USA.