Crystal structure of the GINS complex and functional insights into its role in DNA replication.
Chang, Y.P., Wang, G., Bermudez, V., Hurwitz, J., Chen, X.S.(2007) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104: 12685-12690
- PubMed: 17652513
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0705558104
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2Q9Q - PubMed Abstract:
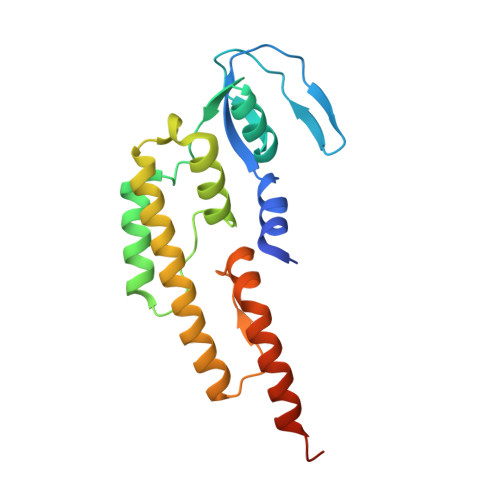
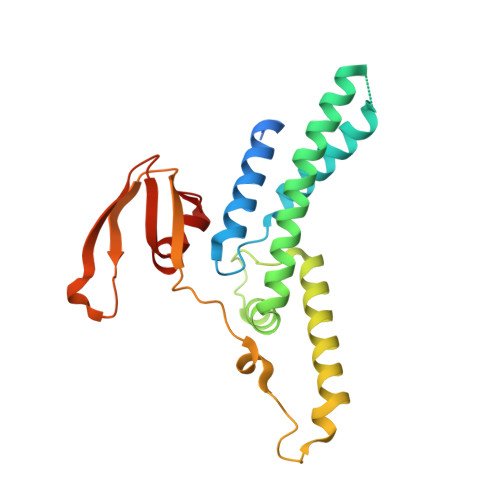
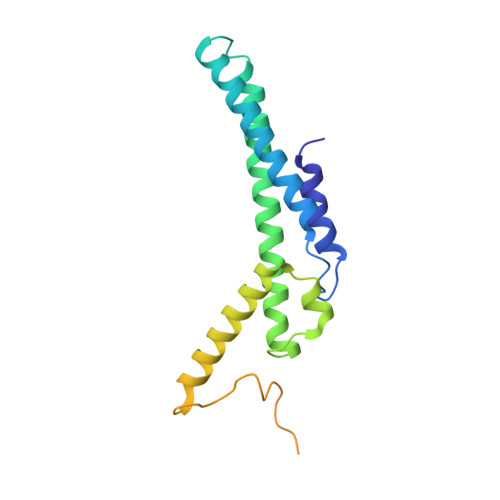
The GINS complex, which contains the four subunits Sld5, Psf1, Psf2, and Psf3, is essential for both the initiation and progression of DNA replication in eukaryotes. GINS associates with the MCM2-7 complex and Cdc45 to activate the eukaryotic minichromosome maintenance helicase. It also appears to interact with and stimulate the polymerase activities of DNA polymerase epsilon and the DNA polymerase alpha-primase complex. To further understand the functional role of GINS, we determined the crystal structure of the full-length human GINS heterotetramer. Each of the four subunits has a major domain composed of an alpha-helical bundle-like structure. With the exception of Psf1, each of the other subunits has a small domain containing a three-stranded beta-sheet core. Each full-length protein in the crystal has unstructured regions that are all located on the surface of GINS and are probably involved in its interaction with other replication factors. The four subunits contact each other mainly through alpha-helices to form a ring-like tetramer with a central pore. This pore is partially plugged by a 16-residue peptide from the Psf3 N terminus, which is unique to some eukaryotic Psf3 proteins and is not required for tetramer formation. Removal of these N-terminal 16 residues of Psf3 from the GINS tetramer increases the opening of the pore by 80%, suggesting a mechanism by which accessibility to the pore may be regulated. The structural data presented here indicate that the GINS tetramer is a highly stable complex with multiple flexible surface regions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Graduate Program in Genetic, Molecular, and Cell Biology, and Section of Molecular and Computational Biology, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA 90089, USA.