Solution Structures of the Linear Leaderless Bacteriocins Enterocin 7A and 7B Resemble Carnocyclin A, a Circular Antimicrobial Peptide
Lohans, C.T., Towle, K.M., Miskolzie, M., McKay, R.T., van Belkum, M.J., McMullen, L.M., Vederas, J.C.(2013) Biochemistry 52: 3987-3994
- PubMed: 23725536
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi400359z
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2M5Z, 2M60 - PubMed Abstract:
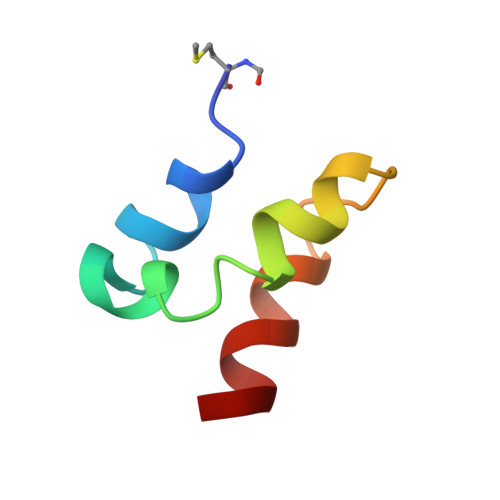
Leaderless bacteriocins are a class of ribosomally synthesized antimicrobial peptides that are produced by certain Gram-positive bacteria without an N-terminal leader section. These bacteriocins are of great interest due to their potent inhibition of many Gram-positive organisms, including food-borne pathogens such as Listeria and Clostridium spp. We now report the NMR solution structures of enterocins 7A and 7B, leaderless bacteriocins recently isolated from Enterococcus faecalis 710C. These are the first three-dimensional structures to be reported for bacteriocins of this class. Unlike most other linear Gram-positive bacteriocins, enterocins 7A and 7B are highly structured in aqueous conditions. Both peptides are primarily α-helical, adopting a similar overall fold. The structures can be divided into three separate α-helical regions: the N- and C-termini are both α-helical, separated by a central kinked α-helix. The overall structures bear an unexpected resemblance to carnocyclin A, a 60-residue peptide that is cyclized via an amide bond between the C- and N-termini and has a saposin fold. Because of synergism observed for other two-peptide leaderless bacteriocins, it was of interest to probe possible binding interactions between enterocins 7A and 7B. However, despite synergistic activity observed between these peptides, no significant binding interaction was observed based on NMR and isothermal calorimetry.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, and §Department of Agricultural, Food and Nutritional Science, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada T6G 2G2.