Isolation, Structure Elucidation, and Synergistic Antibacterial Activity of a Novel Two-Component Lantibiotic Lichenicidin from Bacillus Licheniformis Vk21.
Shenkarev, Z.O., Finkina, E.I., Nurmukhamedova, E.K., Balandin, S.V., Mineev, K.S., Nadezhdin, K.D., Yakimenko, Z.A., Tagaev, A.A., Temirov, Y.V., Arseniev, A.S., Ovchinnikova, T.V.(2010) Biochemistry 49: 6462
- PubMed: 20578714
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi100871b
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2KTO - PubMed Abstract:
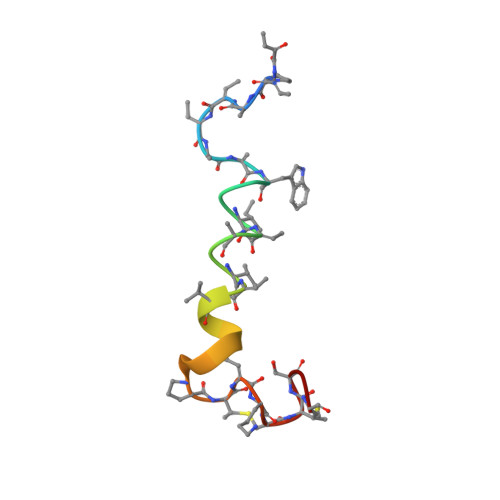
A novel synergetic lantibiotic pair, Lchalpha (3249.51 Da) and Lchbeta (3019.36 Da), termed lichenicidin VK21, was isolated from the producer strain Bacillus licheniformis VK21. Chemical and spatial structures of Lchalpha and Lchbeta were determined. Each peptide contains 31 amino acid residues linked by 4 intramolecular thioether bridges and the N-terminal 2-oxobutyryl group. Spatial structures of Lchalpha and Lchbeta were studied by NMR spectroscopy in methanol solution. The Lchalpha peptide displays structural homology with mersacidin-like lantibiotics and involves relatively well-structured N- and C-terminal domains connected by a flexible loop stabilized by a thioether bridge Ala11-S-Ala21. In contrast, the Lchbeta peptide represents a prolonged hydrophobic alpha-helix flanked with more flexible N- and C-terminal domains. A lantibiotic cluster of the Bacillus licheniformis VK21 genome which comprises the structural genes, lchA1 and lchA2, encoding the lantibiotics precursors, as well as the gene of a modifying enzyme lchM1, was amplified and sequenced. The mature peptides, Lchalpha and Lchbeta, interact synergistically to possess antibiotic activity against Gram-positive bacteria within a nanomolar concentration range, though the individual peptides were shown to be active at micromolar concentrations. Our results afford molecular insight into the mechanism of lichenicidin VK21 action.
Organizational Affiliation:
Shemyakin and Ovchinnikov Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry, Russian Academy of Sciences, Miklukho-Maklaya str. 16/10, Moscow, Russia.